Ниже описана семантика операций, определенных в интерфейсе XlaBuilder . Как правило, эти операции однозначно соответствуют операциям, определенным в интерфейсе RPC в xla_data.proto .
Примечание по номенклатуре: обобщенный тип данных, с которым работает XLA, представляет собой N-мерный массив, содержащий элементы некоторого однородного типа (например, 32-битное число с плавающей запятой). В документации термин «массив» используется для обозначения массива произвольной размерности. Для удобства частные случаи имеют более специфические и привычные названия; например, вектор — это одномерный массив, а матрица — это двумерный массив.
Узнайте больше о структуре операции в разделах «Фигуры и компоновка» и «Плиточная компоновка» .
Пресс
См. также XlaBuilder::Abs .
Поэлементное абсолютное значение x -> |x| .
Abs(operand)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | Операнд функции |
Для получения дополнительной информации о StableHLO см. раздел StableHLO - abs .
Добавлять
См. также XlaBuilder::Add .
Выполняет поэлементное сложение lhs и rhs .
Add(lhs, rhs)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Левый операнд: массив типа T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Левый операнд: массив типа T |
Формы аргументов должны быть либо похожими, либо совместимыми. См. документацию по широковещательной передаче , чтобы узнать, что означает совместимость форм. Результат операции имеет форму, которая является результатом широковещательной передачи двух входных массивов. В этом варианте операции между массивами разного ранга не поддерживаются, за исключением случаев, когда один из операндов является скаляром.
Существует альтернативный вариант с поддержкой многомерного вещания для функции Add:
Add(lhs,rhs, broadcast_dimensions)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Левый операнд: массив типа T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Левый операнд: массив типа T |
| broadcast_dimension | ArraySlice | Какому измерению в целевой форме соответствует каждое измерение формы операнда? |
Этот вариант операции следует использовать для арифметических операций между массивами разного ранга (например, сложение матрицы с вектором).
Дополнительный операнд broadcast_dimensions представляет собой срез целых чисел, определяющий измерения, используемые для трансляции операндов. Семантика подробно описана на странице, посвященной трансляции .
Для получения дополнительной информации о StableHLO см. раздел StableHLO - add .
Добавить зависимость
См. также HloInstruction::AddDependency .
AddDependency может присутствовать в дампах HLO, но его создание вручную конечными пользователями не рекомендуется.
После всего
См. также XlaBuilder::AfterAll .
Функция AfterAll принимает различное количество токенов и выдает один токен. Токены — это примитивные типы данных, которые можно использовать в паре между побочными операциями для обеспечения упорядоченности. AfterAll можно использовать как объединение токенов для упорядочивания операции после набора операций.
AfterAll(tokens)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
tokens | вектор XlaOp | вариативное количество токенов |
Для получения дополнительной информации о StableHLO см. раздел StableHLO - after_all .
AllGather
См. также XlaBuilder::AllGather .
Выполняет конкатенацию между репликами.
AllGather(operand, all_gather_dimension, shard_count, replica_groups, channel_id, layout, use_global_device_ids)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | Массив для объединения данных из нескольких реплик. |
all_gather_dimension | int64 | Размерность конкатенации |
shard_count | int64 | Размер каждой группы реплик |
replica_groups | вектор векторов int64 | Группы, между которыми выполняется конкатенация. |
channel_id | необязательный ChannelHandle | Необязательный идентификатор канала для межмодульной связи. |
layout | необязательная Layout | Создает шаблон компоновки, который будет перехватывать соответствующий шаблон компоновки в аргументе. |
use_global_device_ids | необязательный bool | Возвращает true, если идентификаторы в конфигурации ReplicaGroup представляют собой глобальный идентификатор. |
-
replica_groups— это список групп реплик, между которыми выполняется конкатенация (идентификатор текущей реплики можно получить с помощьюReplicaId). Порядок реплик в каждой группе определяет порядок расположения их входных данных в результате.replica_groupsдолжен быть либо пустым (в этом случае все реплики принадлежат одной группе, упорядоченной от0доN - 1), либо содержать такое же количество элементов, как и количество реплик. Например,replica_groups = {0, 2}, {1, 3}выполняет конкатенацию между репликами0и2, а также1и3. -
shard_count— это размер каждой группы реплик. Он необходим в тех случаях, когдаreplica_groupsпусты. -
channel_idиспользуется для межмодульного взаимодействия: только операцииall-gatherс одинаковымchannel_idмогут обмениваться данными друг с другом. -
use_global_device_idsвозвращает true, если идентификаторы в конфигурации ReplicaGroup представляют собой глобальный идентификатор (replica_id * partition_count + partition_id), а не идентификатор реплики. Это обеспечивает более гибкую группировку устройств, если этот процесс all-reduce выполняется как между разделами, так и между репликами.
Форма выходных данных соответствует форме входных данных, но значение all_gather_dimension увеличено в shard_count раз. Например, если есть две реплики, и операнд имеет значения [1.0, 2.5] и [3.0, 5.25] соответственно на обеих репликах, то выходное значение этой операции, где all_gather_dim равно 0 , будет [1.0, 2.5, 3.0,5.25] на обеих репликах.
API AllGather внутренне разделен на 2 инструкции HLO ( AllGatherStart и AllGatherDone ).
См. также HloInstruction::CreateAllGatherStart .
AllGatherStart и AllGatherDone служат примитивами в HLO. Эти операции могут появляться в дампах HLO, но они не предназначены для создания вручную конечными пользователями.
Для получения дополнительной информации о StableHLO см. раздел StableHLO - all_gather .
AllReduce
См. также XlaBuilder::AllReduce .
Выполняет пользовательские вычисления на нескольких репликах.
AllReduce(operand, computation, replica_groups, channel_id, shape_with_layout, use_global_device_ids)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | Массив или непустой кортеж массивов для уменьшения количества копий при переборе. |
computation | XlaComputation | Вычисление сокращения |
replica_groups | Вектор ReplicaGroup | Группы, между которыми проводятся сокращения |
channel_id | необязательный ChannelHandle | Необязательный идентификатор канала для межмодульной связи. |
shape_with_layout | дополнительная Shape | Определяет структуру передаваемых данных. |
use_global_device_ids | необязательный bool | Возвращает true, если идентификаторы в конфигурации ReplicaGroup представляют собой глобальный идентификатор. |
- Когда
operandпредставляет собой кортеж массивов, операция редукции выполняется для каждого элемента кортежа. -
replica_groups— это список групп реплик, между которыми выполняется сокращение (идентификатор текущей реплики можно получить с помощьюReplicaId).replica_groupsдолжен быть либо пустым (в этом случае все реплики принадлежат одной группе), либо содержать такое же количество элементов, как и количество реплик. Например,replica_groups = {0, 2}, {1, 3}выполняет сокращение между репликами0и2, а также1и3. -
channel_idиспользуется для межмодульного взаимодействия: только операцииall-reduceс одинаковымchannel_idмогут обмениваться данными друг с другом. -
shape_with_layout: принудительно устанавливает заданную структуру данных для операции AllReduce. Это используется для обеспечения одинаковой структуры данных для группы операций AllReduce, скомпилированных отдельно. -
use_global_device_idsвозвращает true, если идентификаторы в конфигурации ReplicaGroup представляют собой глобальный идентификатор (replica_id * partition_count + partition_id), а не идентификатор реплики. Это обеспечивает более гибкую группировку устройств, если этот процесс all-reduce выполняется как между разделами, так и между репликами.
Форма выходных данных совпадает с формой входных данных. Например, если есть две реплики, и операнд имеет значения [1.0, 2.5] и [3.0, 5.25] соответственно на обеих репликах, то выходное значение этой операции и вычисления суммы будет [4.0, 7.75] на обеих репликах. Если входные данные представляют собой кортеж, то и выходные данные также являются кортежами.
Для вычисления результата AllReduce требуется один входной сигнал от каждой реплики, поэтому, если одна реплика выполняет узел AllReduce больше раз, чем другая, то предыдущая реплика будет ждать бесконечно. Поскольку все реплики выполняют одну и ту же программу, существует не так много способов, как это может произойти, но это возможно, когда условие цикла while зависит от данных, поступающих из infeed , и эти infeed заставляют цикл while выполняться больше раз на одной реплике, чем на другой.
API AllReduce внутренне разделен на 2 инструкции HLO ( AllReduceStart и AllReduceDone ).
См. также HloInstruction::CreateAllReduceStart .
AllReduceStart и AllReduceDone служат примитивами в HLO. Эти операции могут появляться в дампах HLO, но они не предназначены для создания вручную конечными пользователями.
CrossReplicaSum
См. также XlaBuilder::CrossReplicaSum .
Выполняет операцию AllReduce с вычислением суммы.
CrossReplicaSum(operand, replica_groups)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | Массив или непустой кортеж массивов для уменьшения количества копий при переборе. |
replica_groups | вектор векторов int64 | Группы, между которыми проводятся сокращения |
Возвращает сумму значений операнда в каждой подгруппе реплик. Все реплики предоставляют один входной параметр для вычисления суммы, и все реплики получают результирующую сумму для каждой подгруппы.
ВсеВсем
См. также XlaBuilder::AllToAll .
AllToAll — это коллективная операция, которая отправляет данные со всех ядер на все ядра. Она состоит из двух фаз:
- Фаза распределения. На каждом ядре операнд разбивается на количество блоков по
split_dimensionssplit_countи эти блоки распределяются по всем ядрам, например, i-й блок отправляется на i-е ядро. - Этап сбора данных. Каждое ядро объединяет полученные блоки вдоль
concat_dimension.
Участвующие ядра можно настроить следующим образом:
-
replica_groups: каждая ReplicaGroup содержит список идентификаторов реплик, участвующих в вычислениях (идентификатор текущей реплики можно получить с помощьюReplicaId). AllToAll будет применяться внутри подгрупп в указанном порядке. Например,replica_groups = { {1,2,3}, {4,5,0} }означает, что AllToAll будет применена внутри реплик{1, 2, 3}на этапе сбора данных, и полученные блоки будут объединены в том же порядке 1, 2, 3. Затем еще одна AllToAll будет применена внутри реплик 4, 5, 0, и порядок объединения также будет 4, 5, 0. Еслиreplica_groupsпуста, все реплики принадлежат одной группе в порядке их появления.
Предварительные требования:
- Размерность операнда в
split_dimensionделится наsplit_count. - Форма операнда не является кортежем.
AllToAll(operand, split_dimension, concat_dimension, split_count, replica_groups, layout, channel_id)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | n-мерный входной массив |
split_dimension | int64 | Значение в интервале [0,n) , указывающее измерение, по которому разделяется операнд. |
concat_dimension | int64 | Значение в интервале [0,n) , указывающее измерение, вдоль которого соединяются разделенные блоки. |
split_count | int64 | Количество ядер, участвующих в этой операции. Если replica_groups пуст, это должно быть количество реплик; в противном случае, это должно быть равно количеству реплик в каждой группе. |
replica_groups | Вектор ReplicaGroup | Каждая группа содержит список идентификаторов реплик. |
layout | необязательная Layout | заданная пользователем структура памяти |
channel_id | необязательный ChannelHandle | уникальный идентификатор для каждой пары отправка/приём |
Дополнительную информацию о формах и макетах см. в разделе xla::shapes.
Для получения дополнительной информации о StableHLO см. раздел StableHLO - all_to_all .
AllToAll - Пример 1.
XlaBuilder b("alltoall");
auto x = Parameter(&b, 0, ShapeUtil::MakeShape(F32, {4, 16}), "x");
AllToAll(
x,
/*split_dimension=*/ 1,
/*concat_dimension=*/ 0,
/*split_count=*/ 4);
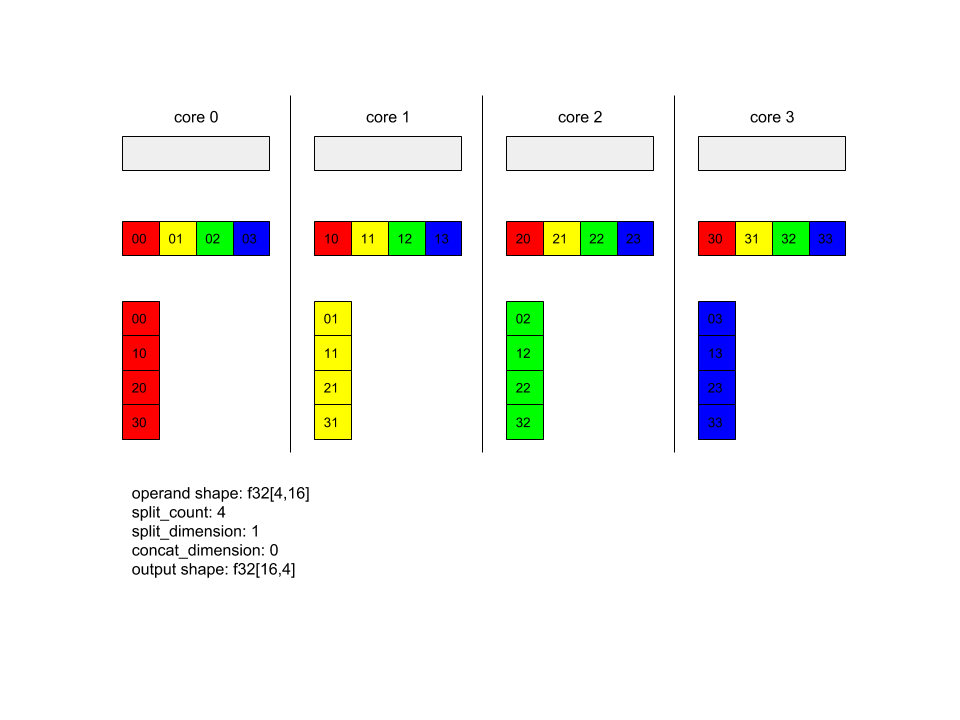
В приведенном выше примере в процессе Alltoall участвуют 4 ядра. На каждом ядре операнд разбивается на 4 части по измерению 1, так что каждая часть имеет форму f32[4,4]. Эти 4 части распределяются по всем ядрам. Затем каждое ядро объединяет полученные части по измерению 0 в порядке ядер 0-4. Таким образом, выходные данные на каждом ядре имеют форму f32[16,4].
AllToAll - Пример 2 - StableHLO
В приведенном выше примере в процессе AllToAll участвуют 2 реплики. На каждой реплике операнд имеет форму f32[2,4]. Операнд разделен на 2 части по измерению 1, поэтому каждая часть имеет форму f32[2,2]. Затем эти 2 части обмениваются между репликами в соответствии с их положением в группе реплик. Каждая реплика собирает соответствующую ей часть из обоих операндов и объединяет их по измерению 0. В результате выходные данные на каждой реплике имеют форму f32[4,2].
RaggedAllToAll
См. также XlaBuilder::RaggedAllToAll .
Функция RaggedAllToAll выполняет коллективную операцию "все ко всем", где входные и выходные данные представляют собой "неровные" тензоры.
RaggedAllToAll(input, input_offsets, send_sizes, output, output_offsets, recv_sizes, replica_groups, channel_id)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
input | XlaOp | N массивов типа Т |
input_offsets | XlaOp | N массивов типа Т |
send_sizes | XlaOp | N массивов типа Т |
output | XlaOp | N массивов типа Т |
output_offsets | XlaOp | N массивов типа Т |
recv_sizes | XlaOp | N массивов типа Т |
replica_groups | Вектор ReplicaGroup | Каждая группа содержит список идентификаторов реплик. |
channel_id | необязательный ChannelHandle | уникальный идентификатор для каждой пары отправка/приём |
Неровные тензоры определяются набором из трех тензоров:
-
data: тензорdataимеет «неровный» характер вдоль своей самой внешней размерности, при этом каждый индексированный элемент имеет переменный размер. -
offsets: тензорoffsetsиндексирует самое внешнее измерение тензораdataи представляет собой начальное смещение каждого неровного элемента тензораdata. -
sizes: тензорsizesпредставляет размер каждого «неровного» элемента тензораdata, где размер задается в единицах подэлементов. Подэлемент определяется как суффикс формы тензора «данных», полученный путем удаления самого внешнего «неровного» измерения. - Тензоры
offsetsиsizesдолжны иметь одинаковый размер.
Пример неровного тензора:
data: [8,3] =
{ {a,b,c},{d,e,f},{g,h,i},{j,k,l},{m,n,o},{p,q,r},{s,t,u},{v,w,x} }
offsets: [3] = {0, 1, 4}
sizes: [3] = {1, 3, 4}
// Index 'data' at 'offsets'[0], 'sizes'[0]' // {a,b,c}
// Index 'data' at 'offsets'[1], 'sizes'[1]' // {d,e,f},{g,h,i},{j,k,l}
// Index 'data' at 'offsets'[2], 'sizes'[2]' // {m,n,o},{p,q,r},{s,t,u},{v,w,x}
output_offsets должен быть распределен таким образом, чтобы каждая реплика имела смещения в перспективе выходных данных целевой реплики.
Для i-го смещения выходного сигнала текущая реплика отправит обновление input[input_offsets[i]:input_offsets[i]+input_sizes[i]] i -й реплике, которое будет записано в output_i[output_offsets[i]:output_offsets[i]+send_sizes[i]] на output i -й реплики.
Например, если у нас есть 2 реплики:
replica 0:
input: [1, 2, 2]
output:[0, 0, 0, 0]
input_offsets: [0, 1]
send_sizes: [1, 2]
output_offsets: [0, 0]
recv_sizes: [1, 1]
replica 1:
input: [3, 4, 0]
output: [0, 0, 0, 0]
input_offsets: [0, 1]
send_sizes: [1, 1]
output_offsets: [1, 2]
recv_sizes: [2, 1]
// replica 0's result will be: [1, 3, 0, 0]
// replica 1's result will be: [2, 2, 4, 0]
Неровный, универсальный HLO имеет следующие аргументы:
-
input: тензор входных данных с неровными краями. -
output: тензор выходных данных с неровными краями. -
input_offsets: тензор с неровными смещениями входных данных. -
send_sizes: тензор размеров для отправки с переменной шириной. -
output_offsets: массив неравномерных смещений на выходе целевой реплики. -
recv_sizes: тензор с неровными размерами возвращаемых значений.
Тензоры *_offsets и *_sizes должны иметь одинаковую форму.
Для тензоров *_offsets и *_sizes поддерживаются две формы:
-
[num_devices]где ragged-all-to-all может отправить не более одного обновления каждому удаленному устройству в группе реплик. Например:
for (remote_device_id : replica_group) {
SEND input[input_offsets[remote_device_id]],
output[output_offsets[remote_device_id]],
send_sizes[remote_device_id] }
[num_devices, num_updates], где ragged-all-to-all может отправлять доnum_updatesобновлений одному и тому же удаленному устройству (каждое с разным смещением) для каждого удаленного устройства в группе реплик.
Например:
for (remote_device_id : replica_group) {
for (update_idx : num_updates) {
SEND input[input_offsets[remote_device_id][update_idx]],
output[output_offsets[remote_device_id][update_idx]]],
send_sizes[remote_device_id][update_idx] } }
И
См. также XlaBuilder::And .
Выполняет поэлементное И двух тензоров lhs и rhs .
And(lhs, rhs)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Левый операнд: массив типа T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Левый операнд: массив типа T |
Формы аргументов должны быть либо похожими, либо совместимыми. См. документацию по широковещательной передаче , чтобы узнать, что означает совместимость форм. Результат операции имеет форму, которая является результатом широковещательной передачи двух входных массивов. В этом варианте операции между массивами разного ранга не поддерживаются, за исключением случаев, когда один из операндов является скаляром.
Существует альтернативный вариант с поддержкой многомерного вещания для And:
And(lhs,rhs, broadcast_dimensions)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Левый операнд: массив типа T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Левый операнд: массив типа T |
| broadcast_dimension | ArraySlice | Какому измерению в целевой форме соответствует каждое измерение формы операнда? |
Этот вариант операции следует использовать для арифметических операций между массивами разного ранга (например, сложение матрицы с вектором).
Дополнительный операнд broadcast_dimensions представляет собой срез целых чисел, определяющий измерения, используемые для трансляции операндов. Семантика подробно описана на странице, посвященной трансляции .
Для получения дополнительной информации о StableHLO см. разделы StableHLO и .
Асинхронный
См. также HloInstruction::CreateAsyncStart , HloInstruction::CreateAsyncUpdate , HloInstruction::CreateAsyncDone .
AsyncDone , AsyncStart и AsyncUpdate — это внутренние инструкции HLO, используемые для асинхронных операций и служащие примитивами в HLO. Эти операции могут появляться в дампах HLO, но они не предназначены для создания вручную конечными пользователями.
Атан2
См. также XlaBuilder::Atan2 .
Выполняет поэлементную операцию atan2 над lhs и rhs .
Atan2(lhs, rhs)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Левый операнд: массив типа T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Левый операнд: массив типа T |
Формы аргументов должны быть либо похожими, либо совместимыми. См. документацию по широковещательной передаче , чтобы узнать, что означает совместимость форм. Результат операции имеет форму, которая является результатом широковещательной передачи двух входных массивов. В этом варианте операции между массивами разного ранга не поддерживаются, за исключением случаев, когда один из операндов является скаляром.
Для Atan2 существует альтернативный вариант с поддержкой многомерного вещания:
Atan2(lhs,rhs, broadcast_dimensions)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Левый операнд: массив типа T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Левый операнд: массив типа T |
| broadcast_dimension | ArraySlice | Какому измерению в целевой форме соответствует каждое измерение формы операнда? |
Этот вариант операции следует использовать для арифметических операций между массивами разного ранга (например, сложение матрицы с вектором).
Дополнительный операнд broadcast_dimensions представляет собой срез целых чисел, определяющий измерения, используемые для трансляции операндов. Семантика подробно описана на странице, посвященной трансляции .
Для получения дополнительной информации о StableHLO см. StableHLO - atan2 .
BatchNormGrad
Подробное описание алгоритма см. также в описании XlaBuilder::BatchNormGrad и в оригинальной статье о пакетной нормализации .
Вычисляет градиенты пакетной нормы.
BatchNormGrad(operand, scale, batch_mean, batch_var, grad_output, epsilon, feature_index)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | n-мерный массив, подлежащий нормализации (x) |
scale | XlaOp | одномерный массив (\(\gamma\)) |
batch_mean | XlaOp | одномерный массив (\(\mu\)) |
batch_var | XlaOp | одномерный массив (\(\sigma^2\)) |
grad_output | XlaOp | Градиенты, передаваемые в BatchNormTraining (\(\nabla y\)) |
epsilon | float | Значение эпсилон (\(\epsilon\)) |
feature_index | int64 | Указатель на измерение признака в operand |
Для каждого признака в измерении признаков ( feature_index — это индекс измерения признаков в operand ) операция вычисляет градиенты относительно operand , offset и scale по всем остальным измерениям. feature_index должен быть допустимым индексом измерения признаков в operand .
Три градиента определяются следующими формулами (при условии использования 4-мерного массива в качестве operand и с индексом размерности признака l , размером пакета m и пространственными размерами w и h ):
\[ \begin{split} c_l&= \frac{1}{mwh}\sum_{i=1}^m\sum_{j=1}^w\sum_{k=1}^h \left( \nabla y_{ijkl} \frac{x_{ijkl} - \mu_l}{\sigma^2_l+\epsilon} \right) \\\\ d_l&= \frac{1}{mwh}\sum_{i=1}^m\sum_{j=1}^w\sum_{k=1}^h \nabla y_{ijkl} \\\\ \nabla x_{ijkl} &= \frac{\gamma_{l} }{\sqrt{\sigma^2_{l}+\epsilon} } \left( \nabla y_{ijkl} - d_l - c_l (x_{ijkl} - \mu_{l}) \right) \\\\ \nabla \gamma_l &= \sum_{i=1}^m\sum_{j=1}^w\sum_{k=1}^h \left( \nabla y_{ijkl} \frac{x_{ijkl} - \mu_l}{\sqrt{\sigma^2_{l}+\epsilon} } \right) \\\\\ \nabla \beta_l &= \sum_{i=1}^m\sum_{j=1}^w\sum_{k=1}^h \nabla y_{ijkl} \end{split} \]
Входные параметры batch_mean и batch_var представляют собой значения моментов по пакету данных и пространственному измерению.
Выходной тип представляет собой кортеж из трех дескрипторов:
| Выходы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
grad_operand | XlaOp | градиент относительно входного operand (\(\nabla x\)) |
grad_scale | XlaOp | градиент относительно входного ** scale ** (\(\nabla\gamma\)) |
grad_offset | XlaOp | градиент относительно входного offset (\(\nabla\beta\)) |
Для получения дополнительной информации о StableHLO см. раздел StableHLO - batch_norm_grad .
BatchNormInference
Подробное описание алгоритма см. также в статье XlaBuilder::BatchNormInference и в оригинальной работе по пакетной нормализации .
Нормализует массив по размерности пакета и пространственному измерению.
BatchNormInference(operand, scale, offset, mean, variance, epsilon, feature_index)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | n-мерный массив, подлежащий нормализации. |
scale | XlaOp | одномерный массив |
offset | XlaOp | одномерный массив |
mean | XlaOp | одномерный массив |
variance | XlaOp | одномерный массив |
epsilon | float | Значение эпсилон |
feature_index | int64 | Указатель на измерение признака в operand |
Для каждого признака в измерении признаков ( feature_index — это индекс измерения признаков в operand ) операция вычисляет среднее значение и дисперсию по всем остальным измерениям и использует эти значения для нормализации каждого элемента в operand . feature_index должен быть допустимым индексом для измерения признаков в operand .
BatchNormInference эквивалентна вызову функции BatchNormTraining без вычисления mean и variance для каждого пакета данных. Вместо этого она использует входные mean и variance в качестве оценочных значений. Цель этой операции — уменьшить задержку при выводе, отсюда и название BatchNormInference .
На выходе получается n-мерный нормализованный массив, имеющий ту же форму, что и входной operand .
Для получения дополнительной информации о StableHLO см. раздел StableHLO - batch_norm_inference .
BatchNormTraining
Подробное описание алгоритма см. также в описании XlaBuilder::BatchNormTraining и the original batch normalization paper .
Нормализует массив по размерности пакета и пространственному измерению.
BatchNormTraining(operand, scale, offset, epsilon, feature_index)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | n-мерный массив, подлежащий нормализации (x) |
scale | XlaOp | одномерный массив (\(\gamma\)) |
offset | XlaOp | одномерный массив (\(\beta\)) |
epsilon | float | Значение эпсилон (\(\epsilon\)) |
feature_index | int64 | Указатель на измерение признака в operand |
Для каждого признака в измерении признаков ( feature_index — это индекс измерения признаков в operand ) операция вычисляет среднее значение и дисперсию по всем остальным измерениям и использует эти значения для нормализации каждого элемента в operand . feature_index должен быть допустимым индексом для измерения признаков в operand .
Алгоритм работает следующим образом для каждой партии в operand \(x\) который содержит m элементов, где w и h — размеры пространственных измерений (предполагая, что operand представляет собой 4-мерный массив):
Вычисляет среднее значение по партии. \(\mu_l\) для каждого признака
lв измерении признаков:\(\mu_l=\frac{1}{mwh}\sum_{i=1}^m\sum_{j=1}^w\sum_{k=1}^h x_{ijkl}\)Вычисляет отклонение партии \(\sigma^2_l\): $\sigma^2 l=\frac{1}{mwh}\sum {i=1}^m\sum {j=1}^w\sum {k=1}^h (x_{ijkl} - \mu_l)^2$
Нормализует, масштабирует и сдвигает:\(y_{ijkl}=\frac{\gamma_l(x_{ijkl}-\mu_l)}{\sqrt[2]{\sigma^2_l+\epsilon} }+\beta_l\)
Значение эпсилон, обычно небольшое число, добавляется для предотвращения ошибок деления на ноль.
Выходной тип представляет собой кортеж из трех XlaOp :
| Выходы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
output | XlaOp | n-мерный массив, имеющий ту же форму, что и входной operand (y). |
batch_mean | XlaOp | одномерный массив (\(\mu\)) |
batch_var | XlaOp | одномерный массив (\(\sigma^2\)) |
Значения batch_mean и batch_var представляют собой моменты, рассчитанные по параметрам пакета и пространственному измерению с использованием приведенных выше формул.
Для получения дополнительной информации о StableHLO см. раздел StableHLO - batch_norm_training .
Биткаст
См. также HloInstruction::CreateBitcast .
Bitcast могут содержаться в дампах HLO, но их не следует создавать вручную конечными пользователями.
BitcastConvertType
См. также XlaBuilder::BitcastConvertType .
Подобно функции tf.bitcast в TensorFlow, выполняет поэлементное преобразование битов из заданной формы данных в целевую форму. Размеры входных и выходных данных должны совпадать: например, элементы s32 преобразуются в элементы f32 с помощью процедуры преобразования битов, а один элемент размером s32 преобразуется в четыре элемента размером s8 . Преобразование битов реализовано как низкоуровневое преобразование, поэтому машины с различными представлениями чисел с плавающей запятой дадут разные результаты.
BitcastConvertType(operand, new_element_type)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | массив типа Т с размерами D |
new_element_type | PrimitiveType | тип U |
Размеры операнда и целевой формы должны совпадать, за исключением последнего размера, который изменится в соотношении размеров примитива до и после преобразования.
Типы элементов источника и назначения не должны быть кортежами.
Для получения дополнительной информации о StableHLO см. раздел StableHLO - bitcast_convert .
Bitcast-преобразование в примитивный тип различной ширины
Инструкция BitcastConvert HLO поддерживает случай, когда размер выходного элемента типа T' не равен размеру входного элемента T Поскольку вся операция концептуально представляет собой битовое преобразование и не изменяет базовые байты, форма выходного элемента должна изменяться. Для B = sizeof(T), B' = sizeof(T') возможны два случая.
Во-первых, когда B > B' , выходная форма получает новый наименьший размер B/B' . Например:
f16[10,2]{1,0} %output = f16[10,2]{1,0} bitcast-convert(f32[10]{0} %input)
Для эффективных скаляров это правило остается тем же:
f16[2]{0} %output = f16[2]{0} bitcast-convert(f32[] %input)
В качестве альтернативы, если B' > B инструкция требует, чтобы последний логический размер входной формы был равен B'/B , и этот размер отбрасывается во время преобразования:
f32[10]{0} %output = f32[10]{0} bitcast-convert(f16[10,2]{1,0} %input)
Обратите внимание, что преобразования между различными разрядными значениями не выполняются поэлементно.
Транслировать
См. также XlaBuilder::Broadcast .
Добавляет измерения к массиву путем дублирования данных в массиве.
Broadcast(operand, broadcast_sizes)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | Массив для дублирования |
broadcast_sizes | ArraySlice<int64> | Размеры новых габаритов |
Новые измерения вставляются слева, то есть, если broadcast_sizes имеет значения {a0, ..., aN} , а форма операнда имеет измерения {b0, ..., bM} , то форма выходных данных имеет измерения {a0, ..., aN, b0, ..., bM} .
Новые измерения индексируются в копии операнда, т.е.
output[i0, ..., iN, j0, ..., jM] = operand[j0, ..., jM]
Например, если operand — скаляр f32 со значением 2.0f , а broadcast_sizes — {2, 3} , то результатом будет массив формы f32[2, 3] , и все значения в результате будут равны 2.0f .
Для получения дополнительной информации о StableHLO см. раздел «StableHLO - broadcast» .
BroadcastInDim
См. также XlaBuilder::BroadcastInDim .
Расширяет размер и количество измерений массива путем дублирования данных в массиве.
BroadcastInDim(operand, out_dim_size, broadcast_dimensions)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | Массив для дублирования |
out_dim_size | ArraySlice<int64> | Размеры габаритов целевой формы |
broadcast_dimensions | ArraySlice<int64> | Какому измерению в целевой форме соответствует каждое измерение формы операнда? |
Аналогично функции Broadcast, но позволяет добавлять измерения в любом месте и расширять существующие измерения с шагом 1.
operand передается в форму, описываемую параметром out_dim_size . Параметр broadcast_dimensions сопоставляет размеры operand с размерами целевой формы, то есть i-й размер операнда сопоставляется с broadcast_dimension[i]-м размером выходной формы. Размеры operand должны иметь размер 1 или совпадать с размером размера выходной формы, в которую они сопоставляются. Оставшиеся размеры заполняются размерами размером 1. Затем передача по вырожденным измерениям осуществляется вдоль этих вырожденных измерений для достижения выходной формы. Семантика подробно описана на странице, посвященной передаче .
Вызов
См. также XlaBuilder::Call .
Выполняет вычисление с заданными аргументами.
Call(computation, operands...)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
computation | XlaComputation | вычисление типа T_0, T_1, ..., T_{N-1} -> S с N параметрами произвольного типа |
operands | последовательность N XlaOp s | N аргументов произвольного типа |
Арность и типы operands должны соответствовать параметрам computation . Допускается отсутствие operands .
CompositeCall
См. также XlaBuilder::CompositeCall .
Инкапсулирует операцию, состоящую из других операций StableHLO, принимающую входные данные и атрибуты composite_attributes и выдающую результаты. Семантика операции реализуется атрибутом decomposition. Составную операцию можно заменить ее декомпозицией без изменения семантики программы. В случаях, когда встраивание декомпозиции не обеспечивает ту же семантику операции, предпочтительнее использовать custom_call.
Поле «Версия» (по умолчанию 0) используется для обозначения момента изменения семантики составного элемента.
Эта операция реализована как kCall с атрибутом is_composite=true . Поле decomposition задается атрибутом computation . Атрибуты интерфейса хранят остальные атрибуты с префиксом composite.
Пример операции CompositeCall:
f32[] call(f32[] %cst), to_apply=%computation, is_composite=true,
frontend_attributes = {
composite.name="foo.bar",
composite.attributes={n = 1 : i32, tensor = dense<1> : tensor<i32>},
composite.version="1"
}
CompositeCall(computation, operands..., name, attributes, version)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
computation | XlaComputation | вычисление типа T_0, T_1, ..., T_{N-1} -> S с N параметрами произвольного типа |
operands | последовательность N XlaOp s | вариативное количество значений |
name | string | название композиции |
attributes | необязательная string | необязательный строковый словарь атрибутов |
version | необязательное int64 | Обновления номера версии и семантики составной операции. |
decomposition операции не является полем с именем, а отображается в виде атрибута to_apply, указывающего на функцию, содержащую реализацию нижнего уровня, например, to_apply=%funcname
Более подробную информацию о композитных и декомпозиционных методах можно найти в спецификации StableHLO .
Cbrt
См. также XlaBuilder::Cbrt .
Поэлементная операция извлечения кубического корня x -> cbrt(x) .
Cbrt(operand)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | Операнд функции |
Cbrt также поддерживает необязательный аргумент result_accuracy :
Cbrt(operand, result_accuracy)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | Операнд функции |
result_accuracy | необязательный ResultAccuracy | Типы точности, которые пользователь может запросить для унарных операций с несколькими реализациями. |
Для получения дополнительной информации о точности result_accuracy см. раздел «Точность результатов» .
Для получения дополнительной информации о StableHLO см. StableHLO - cbrt .
Потолок
См. также XlaBuilder::Ceil .
Поэлементное ceil x -> ⌈x⌉ .
Ceil(operand)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | Операнд функции |
Для получения дополнительной информации о StableHLO см. раздел StableHLO - ceil .
Холески
См. также XlaBuilder::Cholesky .
Вычисляет разложение Холецкого для группы симметричных (эрмитовых) положительно определенных матриц.
Cholesky(a, lower)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
a | XlaOp | Массив комплексных или чисел с плавающей запятой, имеющий более 2 измерений. |
lower | bool | использовать ли верхний или нижний a . |
Если lower true , вычисляет нижнетреугольные матрицы l такие, что $a = l . l^T$. Если lower false , вычисляет верхнетреугольные матрицы u такие, что\(a = u^T . u\).
Входные данные считываются только из нижнего/верхнего a , в зависимости от значения lower . Значения из другого треугольника игнорируются. Выходные данные возвращаются в том же треугольнике; значения в другом треугольнике определяются реализацией и могут быть любыми.
Если a имеет более 2 измерений, a рассматривается как набор матриц, где все измерения, кроме двух второстепенных, являются размерами набора.
Если a не является симметричным (эрмитовым) положительно определенным, результат определяется реализацией.
Для получения дополнительной информации о StableHLO см. StableHLO - cholesky .
Зажим
См. также XlaBuilder::Clamp .
Ограничивает значение операнда диапазоном между минимальным и максимальным значениями.
Clamp(min, operand, max)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
min | XlaOp | массив типа Т |
operand | XlaOp | массив типа Т |
max | XlaOp | массив типа Т |
Принимая операнд, а также минимальное и максимальное значения, функция возвращает операнд, если он находится в диапазоне между минимальным и максимальным значениями, в противном случае возвращает минимальное значение, если операнд находится ниже этого диапазона, или максимальное значение, если операнд находится выше этого диапазона. То есть, clamp(a, x, b) = min(max(a, x), b) .
Все три массива должны иметь одинаковую форму. В качестве альтернативы, в качестве ограниченной формы широковещательной передачи , min и/или max могут быть скаляром типа T
Пример со скалярными значениями min и max :
let operand: s32[3] = {-1, 5, 9};
let min: s32 = 0;
let max: s32 = 6;
==>
Clamp(min, operand, max) = s32[3]{0, 5, 6};
Для получения дополнительной информации о StableHLO см. раздел «StableHLO - clamp» .
Крах
См. также XlaBuilder::Collapse и операцию tf.reshape .
Сводит измерения массива к одному измерению.
Collapse(operand, dimensions)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | массив типа Т |
dimensions | вектор int64 | упорядоченное, последовательное подмножество измерений T. |
Оператор `collapse` заменяет заданное подмножество измерений операнда одним измерением. Входными аргументами являются произвольный массив типа T и вектор индексов измерений, являющийся константой времени компиляции. Индексы измерений должны представлять собой последовательное подмножество измерений типа T, упорядоченное (от низкого к высокому номеру измерения). Таким образом, {0, 1, 2}, {0, 1} или {1, 2} являются допустимыми наборами измерений, но {1, 0} или {0, 2} — нет. Они заменяются одним новым измерением, находящимся в той же позиции в последовательности измерений, что и заменяемые ими измерения, при этом размер нового измерения равен произведению размеров исходных измерений. Наименьшее число измерений в dimensions соответствует самому медленно изменяющемуся измерению (наиболее важному) во вложенном цикле, который сворачивает эти измерения, а наибольшее число измерений соответствует самому быстро изменяющемуся измерению (наиболее незначительному). См. оператор tf.reshape если требуется более общий порядок свертывания.
Например, пусть v — массив из 24 элементов:
let v = f32[4x2x3] { { {10, 11, 12}, {15, 16, 17} },
{ {20, 21, 22}, {25, 26, 27} },
{ {30, 31, 32}, {35, 36, 37} },
{ {40, 41, 42}, {45, 46, 47} } };
// Collapse to a single dimension, leaving one dimension.
let v012 = Collapse(v, {0,1,2});
then v012 == f32[24] {10, 11, 12, 15, 16, 17,
20, 21, 22, 25, 26, 27,
30, 31, 32, 35, 36, 37,
40, 41, 42, 45, 46, 47};
// Collapse the two lower dimensions, leaving two dimensions.
let v01 = Collapse(v, {0,1});
then v01 == f32[4x6] { {10, 11, 12, 15, 16, 17},
{20, 21, 22, 25, 26, 27},
{30, 31, 32, 35, 36, 37},
{40, 41, 42, 45, 46, 47} };
// Collapse the two higher dimensions, leaving two dimensions.
let v12 = Collapse(v, {1,2});
then v12 == f32[8x3] { {10, 11, 12},
{15, 16, 17},
{20, 21, 22},
{25, 26, 27},
{30, 31, 32},
{35, 36, 37},
{40, 41, 42},
{45, 46, 47} };
Клз
См. также XlaBuilder::Clz .
Поэлементный подсчет ведущих нулей.
Clz(operand)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | Операнд функции |
CollectiveBroadcast
См. также XlaBuilder::CollectiveBroadcast .
Передает данные между репликами. Данные отправляются от первой реплики с определенным идентификатором в каждой группе к остальным репликам с тем же идентификатором в той же группе. Если реплика с определенным идентификатором не входит ни в одну группу реплик, выходные данные на этой реплике представляют собой тензор, состоящий из нулей определенной shape .
CollectiveBroadcast(operand, replica_groups, channel_id)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | Операнд функции |
replica_groups | Вектор ReplicaGroup | Каждая группа содержит список идентификаторов реплик. |
channel_id | необязательный ChannelHandle | уникальный идентификатор для каждой пары отправка/приём |
Для получения дополнительной информации о StableHLO см. раздел StableHLO - collective_broadcast .
CollectivePermute
См. также XlaBuilder::CollectivePermute .
CollectivePermute — это коллективная операция, которая отправляет и получает данные между репликами.
CollectivePermute(operand, source_target_pairs, channel_id, inplace)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | n-мерный входной массив |
source_target_pairs | <int64, int64> вектор | Список пар (source_replica_id, target_replica_id). Для каждой пары операнд отправляется от исходной реплики к целевой реплике. |
channel_id | необязательный ChannelHandle | Необязательный идентификатор канала для межмодульной связи. |
inplace | необязательный bool | флаг, указывающий, следует ли выполнять перестановку на месте. |
Обратите внимание, что существуют следующие ограничения на пары source_target_pairs :
- Любые две пары не должны иметь одинаковый идентификатор целевой реплики, а также не должны иметь одинаковый идентификатор исходной реплики.
- Если идентификатор реплики не является целевым ни в одной паре, то выходные данные на этой реплике представляют собой тензор, состоящий из нулей (или нулей), имеющий ту же форму, что и входные данные.
API операции CollectivePermute внутренне разложен на 2 инструкции HLO ( CollectivePermuteStart и CollectivePermuteDone ).
См. также HloInstruction::CreateCollectivePermuteStart .
CollectivePermuteStart и CollectivePermuteDone служат примитивами в HLO. Эти операции могут появляться в дампах HLO, но они не предназначены для создания вручную конечными пользователями.
Для получения дополнительной информации о StableHLO см. раздел StableHLO - collective_permute .
Сравнивать
См. также XlaBuilder::Compare .
Выполняет поэлементное сравнение lhs и rhs следующих элементов:
Уравнение
См. также XlaBuilder::Eq .
Выполняет поэлементное сравнение на равенство lhs и rhs .
\(lhs = rhs\)
Eq(lhs, rhs)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Левый операнд: массив типа T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Левый операнд: массив типа T |
The arguments' shapes have to be either similar or compatible. See the broadcasting documentation about what it means for shapes to be compatible. The result of an operation has a shape which is the result of broadcasting the two input arrays. In this variant, operations between arrays of different ranks are not supported, unless one of the operands is a scalar.
An alternative variant with different-dimensional broadcasting support exists for Eq:
Eq(lhs,rhs, broadcast_dimensions)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| broadcast_dimension | ArraySlice | Which dimension in the target shape each dimension of the operand shape corresponds to |
This variant of the operation should be used for arithmetic operations between arrays of different ranks (such as adding a matrix to a vector).
The additional broadcast_dimensions operand is a slice of integers specifying the dimensions to use for broadcasting the operands. The semantics are described in detail on the broadcasting page .
Support a total order over the floating point numbers exists for Eq, by enforcing:
\[-NaN < -Inf < -Finite < -0 < +0 < +Finite < +Inf < +NaN.\]
EqTotalOrder(lhs,rhs, broadcast_dimensions)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| broadcast_dimension | ArraySlice | Which dimension in the target shape each dimension of the operand shape corresponds to |
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - compare .
Не
See also XlaBuilder::Ne .
Performs element-wise not equal-to comparison of lhs and rhs .
\(lhs != rhs\)
Ne(lhs, rhs)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
The arguments' shapes have to be either similar or compatible. See the broadcasting documentation about what it means for shapes to be compatible. The result of an operation has a shape which is the result of broadcasting the two input arrays. In this variant, operations between arrays of different ranks are not supported, unless one of the operands is a scalar.
An alternative variant with different-dimensional broadcasting support exists for Ne:
Ne(lhs,rhs, broadcast_dimensions)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| broadcast_dimension | ArraySlice | Which dimension in the target shape each dimension of the operand shape corresponds to |
This variant of the operation should be used for arithmetic operations between arrays of different ranks (such as adding a matrix to a vector).
The additional broadcast_dimensions operand is a slice of integers specifying the dimensions to use for broadcasting the operands. The semantics are described in detail on the broadcasting page .
Support a total order over the floating point numbers exists for Ne, by enforcing:
\[-NaN < -Inf < -Finite < -0 < +0 < +Finite < +Inf < +NaN.\]
NeTotalOrder(lhs,rhs, broadcast_dimensions)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| broadcast_dimension | ArraySlice | Which dimension in the target shape each dimension of the operand shape corresponds to |
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - compare .
Ге
See also XlaBuilder::Ge .
Performs element-wise greater-or-equal-than comparison of lhs and rhs .
\(lhs >= rhs\)
Ge(lhs, rhs)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
The arguments' shapes have to be either similar or compatible. See the broadcasting documentation about what it means for shapes to be compatible. The result of an operation has a shape which is the result of broadcasting the two input arrays. In this variant, operations between arrays of different ranks are not supported, unless one of the operands is a scalar.
An alternative variant with different-dimensional broadcasting support exists for Ge:
Ge(lhs,rhs, broadcast_dimensions)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| broadcast_dimension | ArraySlice | Which dimension in the target shape each dimension of the operand shape corresponds to |
This variant of the operation should be used for arithmetic operations between arrays of different ranks (such as adding a matrix to a vector).
The additional broadcast_dimensions operand is a slice of integers specifying the dimensions to use for broadcasting the operands. The semantics are described in detail on the broadcasting page .
Support a total order over the floating point numbers exists for Gt, by enforcing:
\[-NaN < -Inf < -Finite < -0 < +0 < +Finite < +Inf < +NaN.\]
GtTotalOrder(lhs,rhs, broadcast_dimensions)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| broadcast_dimension | ArraySlice | Which dimension in the target shape each dimension of the operand shape corresponds to |
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - compare .
Гт
See also XlaBuilder::Gt .
Performs element-wise greater-than comparison of lhs and rhs .
\(lhs > rhs\)
Gt(lhs, rhs)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
The arguments' shapes have to be either similar or compatible. See the broadcasting documentation about what it means for shapes to be compatible. The result of an operation has a shape which is the result of broadcasting the two input arrays. In this variant, operations between arrays of different ranks are not supported, unless one of the operands is a scalar.
An alternative variant with different-dimensional broadcasting support exists for Gt:
Gt(lhs,rhs, broadcast_dimensions)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| broadcast_dimension | ArraySlice | Which dimension in the target shape each dimension of the operand shape corresponds to |
This variant of the operation should be used for arithmetic operations between arrays of different ranks (such as adding a matrix to a vector).
The additional broadcast_dimensions operand is a slice of integers specifying the dimensions to use for broadcasting the operands. The semantics are described in detail on the broadcasting page .
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - compare .
Ле
See also XlaBuilder::Le .
Performs element-wise less-or-equal-than comparison of lhs and rhs .
\(lhs <= rhs\)
Le(lhs, rhs)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
The arguments' shapes have to be either similar or compatible. See the broadcasting documentation about what it means for shapes to be compatible. The result of an operation has a shape which is the result of broadcasting the two input arrays. In this variant, operations between arrays of different ranks are not supported, unless one of the operands is a scalar.
An alternative variant with different-dimensional broadcasting support exists for Le:
Le(lhs,rhs, broadcast_dimensions)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| broadcast_dimension | ArraySlice | Which dimension in the target shape each dimension of the operand shape corresponds to |
This variant of the operation should be used for arithmetic operations between arrays of different ranks (such as adding a matrix to a vector).
The additional broadcast_dimensions operand is a slice of integers specifying the dimensions to use for broadcasting the operands. The semantics are described in detail on the broadcasting page .
Support a total order over the floating point numbers exists for Le, by enforcing:
\[-NaN < -Inf < -Finite < -0 < +0 < +Finite < +Inf < +NaN.\]
LeTotalOrder(lhs,rhs, broadcast_dimensions)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| broadcast_dimension | ArraySlice | Which dimension in the target shape each dimension of the operand shape corresponds to |
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - compare .
лейтенант
See also XlaBuilder::Lt .
Performs element-wise less-than comparison of lhs and rhs .
\(lhs < rhs\)
Lt(lhs, rhs)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
The arguments' shapes have to be either similar or compatible. See the broadcasting documentation about what it means for shapes to be compatible. The result of an operation has a shape which is the result of broadcasting the two input arrays. In this variant, operations between arrays of different ranks are not supported, unless one of the operands is a scalar.
An alternative variant with different-dimensional broadcasting support exists for Lt:
Lt(lhs,rhs, broadcast_dimensions)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| broadcast_dimension | ArraySlice | Which dimension in the target shape each dimension of the operand shape corresponds to |
This variant of the operation should be used for arithmetic operations between arrays of different ranks (such as adding a matrix to a vector).
The additional broadcast_dimensions operand is a slice of integers specifying the dimensions to use for broadcasting the operands. The semantics are described in detail on the broadcasting page .
Support a total order over the floating point numbers exists for Lt, by enforcing:
\[-NaN < -Inf < -Finite < -0 < +0 < +Finite < +Inf < +NaN.\]
LtTotalOrder(lhs,rhs, broadcast_dimensions)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| broadcast_dimension | ArraySlice | Which dimension in the target shape each dimension of the operand shape corresponds to |
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - compare .
Сложный
See also XlaBuilder::Complex .
Performs element-wise conversion to a complex value from a pair of real and imaginary values, lhs and rhs .
Complex(lhs, rhs)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
The arguments' shapes have to be either similar or compatible. See the broadcasting documentation about what it means for shapes to be compatible. The result of an operation has a shape which is the result of broadcasting the two input arrays. In this variant, operations between arrays of different ranks are not supported, unless one of the operands is a scalar.
An alternative variant with different-dimensional broadcasting support exists for Complex:
Complex(lhs,rhs, broadcast_dimensions)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| broadcast_dimension | ArraySlice | Which dimension in the target shape each dimension of the operand shape corresponds to |
This variant of the operation should be used for arithmetic operations between arrays of different ranks (such as adding a matrix to a vector).
The additional broadcast_dimensions operand is a slice of integers specifying the dimensions to use for broadcasting the operands. The semantics are described in detail on the broadcasting page .
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - complex .
ConcatInDim (Concatenate)
See also XlaBuilder::ConcatInDim .
Concatenate composes an array from multiple array operands. The array has the same number of dimensions as each of the input array operands (which must have the same number of dimensions as each other) and contains the arguments in the order that they were specified.
Concatenate(operands..., dimension)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operands | sequence of N XlaOp | N arrays of type T with dimensions [L0, L1, ...]. Requires N >= 1. |
dimension | int64 | A value in the interval [0, N) that names the dimension to be concatenated between the operands . |
With the exception of dimension all dimensions must be the same. This is because XLA does not support "ragged" arrays. Also note that 0-dimensional values cannot be concatenated (as it's impossible to name the dimension along which the concatenation occurs).
1-dimensional example:
Concat({ {2, 3}, {4, 5}, {6, 7} }, 0)
//Output: {2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}
2-dimensional example:
let a = { {1, 2},
{3, 4},
{5, 6} };
let b = { {7, 8} };
Concat({a, b}, 0)
//Output: { {1, 2},
// {3, 4},
// {5, 6},
// {7, 8} }
Диаграмма:
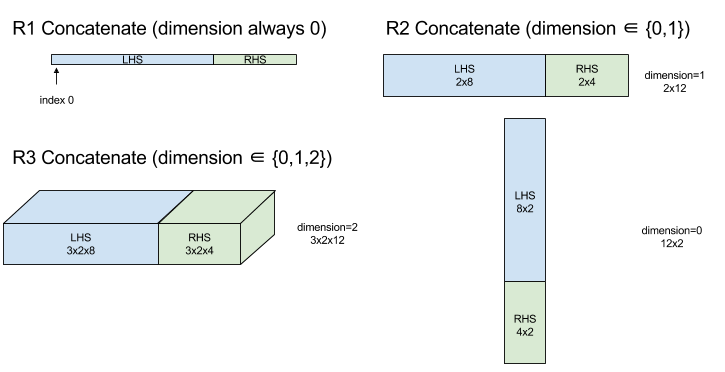
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - concatenate .
Условный
See also XlaBuilder::Conditional .
Conditional(predicate, true_operand, true_computation, false_operand, false_computation)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
predicate | XlaOp | Scalar of type PRED |
true_operand | XlaOp | Argument of type \(T_0\) |
true_computation | XlaComputation | XlaComputation of type \(T_0 \to S\) |
false_operand | XlaOp | Argument of type \(T_1\) |
false_computation | XlaComputation | XlaComputation of type \(T_1 \to S\) |
Executes true_computation if predicate is true , false_computation if predicate is false , and returns the result.
The true_computation must take in a single argument of type \(T_0\) and will be invoked with true_operand which must be of the same type. The false_computation must take in a single argument of type \(T_1\) and will be invoked with false_operand which must be of the same type. The type of the returned value of true_computation and false_computation must be the same.
Note that only one of true_computation and false_computation will be executed depending on the value of predicate .
Conditional(branch_index, branch_computations, branch_operands)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
branch_index | XlaOp | Scalar of type S32 |
branch_computations | sequence of N XlaComputation | XlaComputations of type \(T_0 \to S , T_1 \to S , ..., T_{N-1} \to S\) |
branch_operands | sequence of N XlaOp | Arguments of type \(T_0 , T_1 , ..., T_{N-1}\) |
Executes branch_computations[branch_index] , and returns the result. If branch_index is an S32 which is < 0 or >= N, then branch_computations[N-1] is executed as the default branch.
Each branch_computations[b] must take in a single argument of type \(T_b\) and will be invoked with branch_operands[b] which must be of the same type. The type of the returned value of each branch_computations[b] must be the same.
Note that only one of the branch_computations will be executed depending on the value of branch_index .
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - if .
Постоянный
See also XlaBuilder::ConstantLiteral .
Produces an output from a constant literal .
Constant(literal)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
literal | LiteralSlice | constant view of an existing Literal |
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - constant .
ConvertElementType
See also XlaBuilder::ConvertElementType .
Similar to an element-wise static_cast in C++, ConvertElementType performs an element-wise conversion operation from a data shape to a target shape. The dimensions must match, and the conversion is an element-wise one; eg s32 elements become f32 elements via an s32 -to- f32 conversion routine.
ConvertElementType(operand, new_element_type)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | array of type T with dims D |
new_element_type | PrimitiveType | type U |
The dimensions of the operand and the target shape must match. The source and destination element types must not be tuples.
A conversion such as T=s32 to U=f32 will perform a normalizing int-to-float conversion routine such as round-to-nearest-even.
let a: s32[3] = {0, 1, 2};
let b: f32[3] = convert(a, f32);
then b == f32[3]{0.0, 1.0, 2.0}
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - convert .
Conv (Convolution)
See also XlaBuilder::Conv .
Computes a convolution of the kind used in neural networks. Here, a convolution can be thought of as a n-dimensional window moving across a n-dimensional base area and a computation is performed for each possible position of the window.
Conv Enqueues a convolution instruction onto the computation, which uses the default convolution dimension numbers with no dilation.
The padding is specified in a short-hand way as either SAME or VALID. SAME padding pads the input ( lhs ) with zeroes so that the output has the same shape as the input when not taking striding into account. VALID padding simply means no padding.
Conv(lhs, rhs, window_strides, padding, feature_group_count, batch_group_count, precision_config, preferred_element_type)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
lhs | XlaOp | (n+2)-dimensional array of inputs |
rhs | XlaOp | (n+2)-dimensional array of kernel weights |
window_strides | ArraySlice<int64> | nd array of kernel strides |
padding | Padding | enum of padding |
feature_group_count | int64 | the number of feature groups |
batch_group_count | int64 | the number of batch groups |
precision_config | optional PrecisionConfig | enum for level of precision |
preferred_element_type | optional PrimitiveType | enum of scalar element type |
Increasing levels of controls are available for Conv :
Let n be the number of spatial dimensions. The lhs argument is an (n+2)-dimensional array describing the base area. This is called the input, even though of course the rhs is also an input. In a neural network, these are the input activations. The n+2 dimensions are, in this order:
-
batch: Each coordinate in this dimension represents an independent input for which convolution is carried out. -
z/depth/features: Each (y,x) position in the base area has a vector associated to it, which goes into this dimension. -
spatial_dims: Describes thenspatial dimensions that define the base area that the window moves across.
The rhs argument is an (n+2)-dimensional array describing the convolutional filter/kernel/window. The dimensions are, in this order:
-
output-z: Thezdimension of the output. -
input-z: The size of this dimension timesfeature_group_countshould equal the size of thezdimension in lhs. -
spatial_dims: Describes thenspatial dimensions that define the nd window that moves across the base area.
The window_strides argument specifies the stride of the convolutional window in the spatial dimensions. For example, if the stride in the first spatial dimension is 3, then the window can only be placed at coordinates where the first spatial index is divisible by 3.
The padding argument specifies the amount of zero padding to be applied to the base area. The amount of padding can be negative -- the absolute value of negative padding indicates the number of elements to remove from the specified dimension before doing the convolution. padding[0] specifies the padding for dimension y and padding[1] specifies the padding for dimension x . Each pair has the low padding as the first element and the high padding as the second element. The low padding is applied in the direction of lower indices while the high padding is applied in the direction of higher indices. For example, if padding[1] is (2,3) then there will be a padding by 2 zeroes on the left and by 3 zeroes on the right in the second spatial dimension. Using padding is equivalent to inserting those same zero values into the input ( lhs ) before doing the convolution.
The lhs_dilation and rhs_dilation arguments specify the dilation factor to be applied to the lhs and rhs, respectively, in each spatial dimension. If the dilation factor in a spatial dimension is d, then d-1 holes are implicitly placed between each of the entries in that dimension, increasing the size of the array. The holes are filled with a no-op value, which for convolution means zeroes.
Dilation of the rhs is also called atrous convolution. For more details, see tf.nn.atrous_conv2d . Dilation of the lhs is also called transposed convolution. For more details, see tf.nn.conv2d_transpose .
The feature_group_count argument (default value 1) can be used for grouped convolutions. feature_group_count needs to be a divisor of both the input and the output feature dimension. If feature_group_count is greater than 1, it means that conceptually the input and output feature dimension and the rhs output feature dimension are split evenly into many feature_group_count groups, each group consisting of a consecutive subsequence of features. The input feature dimension of rhs needs to be equal to the lhs input feature dimension divided by feature_group_count (so it already has the size of a group of input features). The i-th groups are used together to compute feature_group_count for many separate convolutions. The results of these convolutions are concatenated together in the output feature dimension.
For depthwise convolution the feature_group_count argument would be set to the input feature dimension, and the filter would be reshaped from [filter_height, filter_width, in_channels, channel_multiplier] to [filter_height, filter_width, 1, in_channels * channel_multiplier] . For more details, see tf.nn.depthwise_conv2d .
The batch_group_count (default value 1) argument can be used for grouped filters during backpropagation. batch_group_count needs to be a divisor of the size of the lhs (input) batch dimension. If batch_group_count is greater than 1, it means that the output batch dimension should be of size input batch / batch_group_count . The batch_group_count must be a divisor of the output feature size.
The output shape has these dimensions, in this order:
-
batch: The size of this dimension timesbatch_group_countshould equal the size of thebatchdimension in lhs. -
z: Same size asoutput-zon the kernel (rhs). -
spatial_dims: One value for each valid placement of the convolutional window.
The figure above shows how the batch_group_count field works. Effectively, we slice each lhs batch into batch_group_count groups, and do the same for the output features. Then, for each of these groups we do pairwise convolutions and concatenate the output along the output feature dimension. The operational semantics of all the other dimensions (feature and spatial) remain the same.
The valid placements of the convolutional window are determined by the strides and the size of the base area after padding.
To describe what a convolution does, consider a 2d convolution, and pick some fixed batch , z , y , x coordinates in the output. Then (y,x) is a position of a corner of the window within the base area (eg the upper left corner, depending on how you interpret the spatial dimensions). We now have a 2d window, taken from the base area, where each 2d point is associated to a 1d vector, so we get a 3d box. From the convolutional kernel, since we fixed the output coordinate z , we also have a 3d box. The two boxes have the same dimensions, so we can take the sum of the element-wise products between the two boxes (similar to a dot product). That is the output value.
Note that if output-z is eg, 5, then each position of the window produces 5 values in the output into the z dimension of the output. These values differ in what part of the convolutional kernel is used - there is a separate 3d box of values used for each output-z coordinate. So you could think of it as 5 separate convolutions with a different filter for each of them.
Here is pseudo-code for a 2d convolution with padding and striding:
for (b, oz, oy, ox) { // output coordinates
value = 0;
for (iz, ky, kx) { // kernel coordinates and input z
iy = oy*stride_y + ky - pad_low_y;
ix = ox*stride_x + kx - pad_low_x;
if ((iy, ix) inside the base area considered without padding) {
value += input(b, iz, iy, ix) * kernel(oz, iz, ky, kx);
}
}
output(b, oz, oy, ox) = value;
}
precision_config is used to indicate the precision configuration. The level dictates whether hardware should attempt to generate more machine code instructions to provide more accurate dtype emulation when needed (ie emulating f32 on a TPU that only supports bf16 matmuls). Values may be DEFAULT , HIGH , HIGHEST . Additional details in the MXU sections .
preferred_element_type is a scalar element of higher/lower precision output types used for accumulation. preferred_element_type recommends the accumulation type for the given operation, however it is not guaranteed. This allows for some hardware backends to instead accumulate in a different type and convert to the preferred output type.
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - convolution .
ConvWithGeneralPadding
See also XlaBuilder::ConvWithGeneralPadding .
ConvWithGeneralPadding(lhs, rhs, window_strides, padding, feature_group_count, batch_group_count, precision_config, preferred_element_type)
Same as Conv where padding configuration is explicit.
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
lhs | XlaOp | (n+2)-dimensional array of inputs |
rhs | XlaOp | (n+2)-dimensional array of kernel weights |
window_strides | ArraySlice<int64> | nd array of kernel strides |
padding | ArraySlice< pair<int64,int64>> | nd array of (low, high) padding |
feature_group_count | int64 | the number of feature groups |
batch_group_count | int64 | the number of batch groups |
precision_config | optional PrecisionConfig | enum for level of precision |
preferred_element_type | optional PrimitiveType | enum of scalar element type |
ConvWithGeneralDimensions
See also XlaBuilder::ConvWithGeneralDimensions .
ConvWithGeneralDimensions(lhs, rhs, window_strides, padding, dimension_numbers, feature_group_count, batch_group_count, precision_config, preferred_element_type)
Same as Conv where dimension numbers are explicit.
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
lhs | XlaOp | (n+2)-dimensional array of inputs |
rhs | XlaOp | (n+2)-dimensional array of kernel weights |
window_strides | ArraySlice<int64> | nd array of kernel strides |
padding | Padding | enum of padding |
dimension_numbers | ConvolutionDimensionNumbers | the number of dimensions |
feature_group_count | int64 | the number of feature groups |
batch_group_count | int64 | the number of batch groups |
precision_config | optional PrecisionConfig | enum for level of precision |
preferred_element_type | optional PrimitiveType | enum of scalar element type |
ConvGeneral
See also XlaBuilder::ConvGeneral .
ConvGeneral(lhs, rhs, window_strides, padding, dimension_numbers, feature_group_count, batch_group_count, precision_config, preferred_element_type)
Same as Conv where dimension numbers and padding configuration is explicit
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
lhs | XlaOp | (n+2)-dimensional array of inputs |
rhs | XlaOp | (n+2)-dimensional array of kernel weights |
window_strides | ArraySlice<int64> | nd array of kernel strides |
padding | ArraySlice< pair<int64,int64>> | nd array of (low, high) padding |
dimension_numbers | ConvolutionDimensionNumbers | the number of dimensions |
feature_group_count | int64 | the number of feature groups |
batch_group_count | int64 | the number of batch groups |
precision_config | optional PrecisionConfig | enum for level of precision |
preferred_element_type | optional PrimitiveType | enum of scalar element type |
ConvGeneralDilated
See also XlaBuilder::ConvGeneralDilated .
ConvGeneralDilated(lhs, rhs, window_strides, padding, lhs_dilation, rhs_dilation, dimension_numbers, feature_group_count, batch_group_count, precision_config, preferred_element_type, window_reversal)
Same as Conv where padding configuration, dilation factors, and dimension numbers are explicit.
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
lhs | XlaOp | (n+2)-dimensional array of inputs |
rhs | XlaOp | (n+2)-dimensional array of kernel weights |
window_strides | ArraySlice<int64> | nd array of kernel strides |
padding | ArraySlice< pair<int64,int64>> | nd array of (low, high) padding |
lhs_dilation | ArraySlice<int64> | nd lhs dilation factor array |
rhs_dilation | ArraySlice<int64> | nd rhs dilation factor array |
dimension_numbers | ConvolutionDimensionNumbers | the number of dimensions |
feature_group_count | int64 | the number of feature groups |
batch_group_count | int64 | the number of batch groups |
precision_config | optional PrecisionConfig | enum for level of precision |
preferred_element_type | optional PrimitiveType | enum of scalar element type |
window_reversal | optional vector<bool> | flag used to logically reverse dimension before applying the convolution |
Копия
See also HloInstruction::CreateCopyStart .
Copy is internally decomposed into 2 HLO instructions CopyStart and CopyDone . Copy along with CopyStart and CopyDone serve as primitives in HLO. These ops may appear in HLO dumps, but they are not intended to be constructed manually by end users.
Кос
See also XlaBuilder::Cos .
Element-wise cosine x -> cos(x) .
Cos(operand)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to the function |
Cos also supports the optional result_accuracy argument:
Cos(operand, result_accuracy)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to the function |
result_accuracy | optional ResultAccuracy | The types of accuracy the user can request for unary ops with multiple implementations |
For more information on result_accuracy see Result Accuracy .
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - cosine .
Кош
See also XlaBuilder::Cosh .
Element-wise hyperbolic cosine x -> cosh(x) .
Cosh(operand)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to the function |
Cosh also supports the optional result_accuracy argument:
Cosh(operand, result_accuracy)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to the function |
result_accuracy | optional ResultAccuracy | The types of accuracy the user can request for unary ops with multiple implementations |
For more information on result_accuracy see Result Accuracy .
CustomCall
See also XlaBuilder::CustomCall .
Call a user-provided function within a computation.
CustomCall documentation is provided in Developer details - XLA Custom Calls
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - custom_call .
Див
See also XlaBuilder::Div .
Performs element-wise division of dividend lhs and divisor rhs .
Div(lhs, rhs)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
Integer division overflow (signed/unsigned division/remainder by zero or signed division/remainder of INT_SMIN with -1 ) produces an implementation defined value.
The arguments' shapes have to be either similar or compatible. See the broadcasting documentation about what it means for shapes to be compatible. The result of an operation has a shape which is the result of broadcasting the two input arrays. In this variant, operations between arrays of different ranks are not supported, unless one of the operands is a scalar.
An alternative variant with different-dimensional broadcasting support exists for Div:
Div(lhs,rhs, broadcast_dimensions)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| broadcast_dimension | ArraySlice | Which dimension in the target shape each dimension of the operand shape corresponds to |
This variant of the operation should be used for arithmetic operations between arrays of different ranks (such as adding a matrix to a vector).
The additional broadcast_dimensions operand is a slice of integers specifying the dimensions to use for broadcasting the operands. The semantics are described in detail on the broadcasting page .
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - divide .
Домен
See also HloInstruction::CreateDomain .
Domain may appear in HLO dumps, but it is not intended to be constructed manually by end users.
Точка
See also XlaBuilder::Dot .
Dot(lhs, rhs, precision_config, preferred_element_type)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
lhs | XlaOp | array of type T |
rhs | XlaOp | array of type T |
precision_config | optional PrecisionConfig | enum for level of precision |
preferred_element_type | optional PrimitiveType | enum of scalar element type |
The exact semantics of this operation depend on the ranks of the operands:
| Вход | Выход | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
vector [n] dot vector [n] | скаляр | векторное скалярное произведение |
matrix [mxk] dot vector [k] | vector [m] | matrix-vector multiplication |
matrix [mxk] dot matrix [kxn] | matrix [mxn] | matrix-matrix multiplication |
The operation performs sum of products over the second dimension of lhs (or the first if it has 1 dimension) and the first dimension of rhs . These are the "contracted" dimensions. The contracted dimensions of lhs and rhs must be of the same size. In practice, it can be used to perform dot products between vectors, vector/matrix multiplications or matrix/matrix multiplications.
precision_config is used to indicate the precision configuration. The level dictates whether hardware should attempt to generate more machine code instructions to provide more accurate dtype emulation when needed (ie emulating f32 on a TPU that only supports bf16 matmuls). Values may be DEFAULT , HIGH , HIGHEST . Additional details in the MXU sections .
preferred_element_type is a scalar element of higher/lower precision output types used for accumulation. preferred_element_type recommends the accumulation type for the given operation, however it is not guaranteed. This allows for some hardware backends to instead accumulate in a different type and convert to the preferred output type.
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - dot .
DotGeneral
See also XlaBuilder::DotGeneral .
DotGeneral(lhs, rhs, dimension_numbers, precision_config, preferred_element_type)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
lhs | XlaOp | array of type T |
rhs | XlaOp | array of type T |
dimension_numbers | DotDimensionNumbers | contracting and batch dimension numbers |
precision_config | optional PrecisionConfig | enum for level of precision |
preferred_element_type | optional PrimitiveType | enum of scalar element type |
Similar to Dot, but allows contracting and batch dimension numbers to be specified for both the lhs and rhs .
| DotDimensionNumbers Fields | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
lhs_contracting_dimensions | repeated int64 | lhs contracting dimension numbers |
rhs_contracting_dimensions | repeated int64 | rhs contracting dimension numbers |
lhs_batch_dimensions | repeated int64 | lhs batch dimension numbers |
rhs_batch_dimensions | repeated int64 | rhs batch dimension numbers |
DotGeneral performs the sum of products over contracting dimensions specified in dimension_numbers .
Associated contracting dimension numbers from the lhs and rhs do not need to be the same but must have the same dimension sizes.
Example with contracting dimension numbers:
lhs = { {1.0, 2.0, 3.0},
{4.0, 5.0, 6.0} }
rhs = { {1.0, 1.0, 1.0},
{2.0, 2.0, 2.0} }
DotDimensionNumbers dnums;
dnums.add_lhs_contracting_dimensions(1);
dnums.add_rhs_contracting_dimensions(1);
DotGeneral(lhs, rhs, dnums) -> { { 6.0, 12.0},
{15.0, 30.0} }
Associated batch dimension numbers from the lhs and rhs must have the same dimension sizes.
Example with batch dimension numbers (batch size 2, 2x2 matrices):
lhs = { { {1.0, 2.0},
{3.0, 4.0} },
{ {5.0, 6.0},
{7.0, 8.0} } }
rhs = { { {1.0, 0.0},
{0.0, 1.0} },
{ {1.0, 0.0},
{0.0, 1.0} } }
DotDimensionNumbers dnums;
dnums.add_lhs_contracting_dimensions(2);
dnums.add_rhs_contracting_dimensions(1);
dnums.add_lhs_batch_dimensions(0);
dnums.add_rhs_batch_dimensions(0);
DotGeneral(lhs, rhs, dnums) -> {
{ {1.0, 2.0},
{3.0, 4.0} },
{ {5.0, 6.0},
{7.0, 8.0} } }
| Вход | Выход | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
[b0, m, k] dot [b0, k, n] | [b0, m, n] | batch matmul |
[b0, b1, m, k] dot [b0, b1, k, n] | [b0, b1, m, n] | batch matmul |
It follows that the resulting dimension number starts with the batch dimension, then the lhs non-contracting/non-batch dimension, and finally the rhs non-contracting/non-batch dimension.
precision_config is used to indicate the precision configuration. The level dictates whether hardware should attempt to generate more machine code instructions to provide more accurate dtype emulation when needed (ie emulating f32 on a TPU that only supports bf16 matmuls). Values may be DEFAULT , HIGH , HIGHEST . Additional details can be found in the MXU sections .
preferred_element_type is a scalar element of higher/lower precision output types used for accumulation. preferred_element_type recommends the accumulation type for the given operation, however it is not guaranteed. This allows for some hardware backends to instead accumulate in a different type and convert to the preferred output type.
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - dot_general .
ScaledDot
See also XlaBuilder::ScaledDot .
ScaledDot(lhs, lhs_scale, rhs, rhs_scale, dimension_number, precision_config,preferred_element_type)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
lhs | XlaOp | array of type T |
rhs | XlaOp | array of type T |
lhs_scale | XlaOp | array of type T |
rhs_scale | XlaOp | array of type T |
dimension_number | ScatterDimensionNumbers | Dimension numbers for scatter operation |
precision_config | PrecisionConfig | enum for level of precision |
preferred_element_type | optional PrimitiveType | enum of scalar element type |
Similar to DotGeneral .
Creates a scaled dot op with operands 'lhs', 'lhs_scale', 'rhs', and 'rhs_scale', with contracting and batch dimensions specified in 'dimension_numbers'.
RaggedDot
See also XlaBuilder::RaggedDot .
For a breakdown of RaggedDot computation see StableHLO - chlo.ragged_dot
DynamicReshape
See also XlaBuilder::DynamicReshape .
This operation is functionally identical to reshape , but the result shape is specified dynamically via output_shape.
DynamicReshape(operand, dim_sizes, new_size_bounds, dims_are_dynamic)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | N dimensional array of type T |
dim_sizes | vector of XlaOP | N dimensional vector sizes |
new_size_bounds | vector of int63 | N dimensional vector of bounds |
dims_are_dynamic | vector of bool | N dimensional dynamic dim |
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - dynamic_reshape .
DynamicSlice
See also XlaBuilder::DynamicSlice .
DynamicSlice extracts a sub-array from the input array at dynamic start_indices . The size of the slice in each dimension is passed in size_indices , which specify the end point of exclusive slice intervals in each dimension: [start, start + size). The shape of start_indices must be 1-dimensional, with dimension size equal to the number of dimensions of operand .
DynamicSlice(operand, start_indices, slice_sizes)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | N dimensional array of type T |
start_indices | sequence of N XlaOp | List of N scalar integers containing the starting indices of the slice for each dimension. Value must be greater than or equal to zero. |
size_indices | ArraySlice<int64> | List of N integers containing the slice size for each dimension. Each value must be strictly greater than zero, and start + size must be less than or equal to the size of the dimension to avoid wrapping modulo dimension size. |
The effective slice indices are computed by applying the following transformation for each index i in [1, N) before performing the slice:
start_indices[i] = clamp(start_indices[i], 0, operand.dimension_size[i] - slice_sizes[i])
This ensures that the extracted slice is always in-bounds with respect to the operand array. If the slice is in-bounds before the transformation is applied, the transformation has no effect.
1-dimensional example:
let a = {0.0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0};
let s = {2};
DynamicSlice(a, s, {2});
// Result: {2.0, 3.0}
2-dimensional example:
let b =
{ {0.0, 1.0, 2.0},
{3.0, 4.0, 5.0},
{6.0, 7.0, 8.0},
{9.0, 10.0, 11.0} }
let s = {2, 1}
DynamicSlice(b, s, {2, 2});
//Result:
// { { 7.0, 8.0},
// {10.0, 11.0} }
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - dynamic_slice .
DynamicUpdateSlice
See also XlaBuilder::DynamicUpdateSlice .
DynamicUpdateSlice generates a result which is the value of the input array operand , with a slice update overwritten at start_indices . The shape of update determines the shape of the sub-array of the result which is updated. The shape of start_indices must be 1-dimensional, with dimension size equal to the number of dimensions of operand .
DynamicUpdateSlice(operand, update, start_indices)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | N dimensional array of type T |
update | XlaOp | N dimensional array of type T containing the slice update. Each dimension of update shape must be strictly greater than zero, and start + update must be less than or equal to the operand size for each dimension to avoid generating out-of-bounds update indices. |
start_indices | sequence of N XlaOp | List of N scalar integers containing the starting indices of the slice for each dimension. Value must be greater than or equal to zero. |
The effective slice indices are computed by applying the following transformation for each index i in [1, N) before performing the slice:
start_indices[i] = clamp(start_indices[i], 0, operand.dimension_size[i] - update.dimension_size[i])
This ensures that the updated slice is always in-bounds with respect to the operand array. If the slice is in-bounds before the transformation is applied, the transformation has no effect.
1-dimensional example:
let a = {0.0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0}
let u = {5.0, 6.0}
let s = {2}
DynamicUpdateSlice(a, u, s)
// Result: {0.0, 1.0, 5.0, 6.0, 4.0}
2-dimensional example:
let b =
{ {0.0, 1.0, 2.0},
{3.0, 4.0, 5.0},
{6.0, 7.0, 8.0},
{9.0, 10.0, 11.0} }
let u =
{ {12.0, 13.0},
{14.0, 15.0},
{16.0, 17.0} }
let s = {1, 1}
DynamicUpdateSlice(b, u, s)
// Result:
// { {0.0, 1.0, 2.0},
// {3.0, 12.0, 13.0},
// {6.0, 14.0, 15.0},
// {9.0, 16.0, 17.0} }
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - dynamic_update_slice .
Эрф
See also XlaBuilder::Erf .
Element-wise error function x -> erf(x) where:
\(\text{erf}(x) = \frac{2}{\sqrt{\pi} }\int_0^x e^{-t^2} \, dt\).
Erf(operand)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to the function |
Erf also supports the optional result_accuracy argument:
Erf(operand, result_accuracy)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to the function |
result_accuracy | optional ResultAccuracy | The types of accuracy the user can request for unary ops with multiple implementations |
For more information on result_accuracy see Result Accuracy .
Эксп
See also XlaBuilder::Exp .
Element-wise natural exponential x -> e^x .
Exp(operand)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to the function |
Exp also supports the optional result_accuracy argument:
Exp(operand, result_accuracy)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to the function |
result_accuracy | optional ResultAccuracy | The types of accuracy the user can request for unary ops with multiple implementations |
For more information on result_accuracy see Result Accuracy .
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - exponential .
Эксп1
See also XlaBuilder::Expm1 .
Element-wise natural exponential minus one x -> e^x - 1 .
Expm1(operand)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to the function |
Expm1 also supports the optional result_accuracy argument:
Expm1(operand, result_accuracy)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to the function |
result_accuracy | optional ResultAccuracy | The types of accuracy the user can request for unary ops with multiple implementations |
For more information on result_accuracy see Result Accuracy .
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - exponential_minus_one .
ФФТ
See also XlaBuilder::Fft .
The XLA FFT operation implements the forward and inverse Fourier Transforms for real and complex inputs/outputs. Multidimensional FFTs on up to 3 axes are supported.
Fft(operand, ftt_type, fft_length)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The array we are Fourier transforming. |
fft_type | FftType | См. таблицу ниже. |
fft_length | ArraySlice<int64> | The time-domain lengths of the axes being transformed. This is needed in particular for IRFFT to right-size the innermost axis, since RFFT(fft_length=[16]) has the same output shape as RFFT(fft_length=[17]) . |
FftType | Семантика |
|---|---|
FFT | Forward complex-to-complex FFT. Shape is unchanged. |
IFFT | Inverse complex-to-complex FFT. Shape is unchanged. |
RFFT | Forward real-to-complex FFT. Shape of the innermost axis is reduced to fft_length[-1] // 2 + 1 if fft_length[-1] is a non-zero value, omitting the reversed conjugate part of the transformed signal beyond the Nyquist frequency. |
IRFFT | Inverse real-to-complex FFT (ie takes complex, returns real). Shape of the innermost axis is expanded to fft_length[-1] if fft_length[-1] is a non-zero value, inferring the part of the transformed signal beyond the Nyquist frequency from the reverse conjugate of the 1 to fft_length[-1] // 2 + 1 entries. |
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - fft .
Multidimensional FFT
When more than 1 fft_length is provided, this is equivalent to applying a cascade of FFT operations to each of the innermost axes. Note that for the real->complex and complex->real cases, the innermost axis transform is (effectively) performed first (RFFT; last for IRFFT), which is why the innermost axis is the one which changes size. Other axis transforms will then be complex->complex.
Детали реализации
CPU FFT is backed by Eigen's TensorFFT. GPU FFT uses cuFFT.
Пол
See also XlaBuilder::Floor .
Element-wise floor x -> ⌊x⌋ .
Floor(operand)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to the function |
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - floor .
Слияние
See also HloInstruction::CreateFusion .
Fusion operation represents HLO instructions and serves as a primitive in HLO. This op may appear in HLO dumps but is not intended to be constructed manually by end users.
Собирать
The XLA gather operation stitches together several slices (each slice at a potentially different runtime offset) of an input array.
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - gather .
General Semantics
See also XlaBuilder::Gather . For a more intuitive description, see the "Informal Description" section below.
gather(operand, start_indices, dimension_numbers, slice_sizes, indices_are_sorted)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The array we're gathering from. |
start_indices | XlaOp | Array containing the starting indices of the slices we gather. |
dimension_numbers | GatherDimensionNumbers | The dimension in start_indices that "contains" the starting indices. See below for a detailed description. |
slice_sizes | ArraySlice<int64> | slice_sizes[i] is the bounds for the slice on dimension i . |
indices_are_sorted | bool | Whether the indices are guaranteed to be sorted by the caller. |
For convenience, we label dimensions in the output array not in offset_dims as batch_dims .
The output is an array with batch_dims.size + offset_dims.size dimensions.
The operand.rank must equal the sum of offset_dims.size and collapsed_slice_dims.size . Also, slice_sizes.size has to be equal to operand.rank .
If index_vector_dim is equal to start_indices.rank we implicitly consider start_indices to have a trailing 1 dimension (ie if start_indices was of shape [6,7] and index_vector_dim is 2 then we implicitly consider the shape of start_indices to be [6,7,1] ).
The bounds for the output array along dimension i is computed as follows:
If
iis present inbatch_dims(ie is equal tobatch_dims[k]for somek) then we pick the corresponding dimension bounds out ofstart_indices.shape, skippingindex_vector_dim(ie pickstart_indices.shape.dims[k] ifk<index_vector_dimandstart_indices.shape.dims[k+1] otherwise).If
iis present inoffset_dims(ie equal tooffset_dims[k] for somek) then we pick the corresponding bound out ofslice_sizesafter accounting forcollapsed_slice_dims(ie we pickadjusted_slice_sizes[k] whereadjusted_slice_sizesisslice_sizeswith the bounds at indicescollapsed_slice_dimsremoved).
Formally, the operand index In corresponding to a given output index Out is calculated as follows:
Let
G= {Out[k] forkinbatch_dims}. UseGto slice out a vectorSsuch thatS[i] =start_indices[Combine(G,i)] where Combine(A, b) inserts b at positionindex_vector_diminto A. Note that this is well defined even ifGis empty: IfGis empty thenS=start_indices.Create a starting index,
Sin, intooperandusingSby scatteringSusingstart_index_map. More precisely:Sin[start_index_map[k]] =S[k] ifk<start_index_map.size.Sin[_] =0otherwise.
Create an index
Oinintooperandby scattering the indices at the offset dimensions inOutaccording to thecollapsed_slice_dimsset. More precisely:Oin[remapped_offset_dims(k)] =Out[offset_dims[k]] ifk<offset_dims.size(remapped_offset_dimsis defined below).Oin[_] =0otherwise.
InisOin+Sinwhere + is element-wise addition.
remapped_offset_dims is a monotonic function with domain [ 0 , offset_dims.size ) and range [ 0 , operand.rank ) \ collapsed_slice_dims . So if, eg, offset_dims.size is 4 , operand.rank is 6 and collapsed_slice_dims is { 0 , 2 } then remapped_offset_dims is { 0 → 1 , 1 → 3 , 2 → 4 , 3 → 5 }.
If indices_are_sorted is set to true then XLA can assume that start_indices are sorted (in ascending order, after scattering its values according to start_index_map ) by the user. If they are not then the semantics are implementation defined.
Informal Description and Examples
Informally, every index Out in the output array corresponds to an element E in the operand array, computed as follows:
We use the batch dimensions in
Outto look up a starting index fromstart_indices.We use
start_index_mapto map the starting index (whose size may be less than operand.rank) to a "full" starting index into theoperand.We dynamic-slice out a slice with size
slice_sizesusing the full starting index.We reshape the slice by collapsing the
collapsed_slice_dimsdimensions. Since all collapsed slice dimensions must have a bound of 1, this reshape is always legal.We use the offset dimensions in
Outto index into this slice to get the input element,E, corresponding to output indexOut.
index_vector_dim is set to start_indices.rank - 1 in all of the examples that follow. More interesting values for index_vector_dim do not change the operation fundamentally, but make the visual representation more cumbersome.
To get an intuition on how all of the above fits together, let's look at an example that gathers 5 slices of shape [8,6] from a [16,11] array. The position of a slice into the [16,11] array can be represented as an index vector of shape S64[2] , so the set of 5 positions can be represented as a S64[5,2] array.
The behavior of the gather operation can then be depicted as an index transformation that takes [ G , O 0 , O 1 ], an index in the output shape, and maps it to an element in the input array in the following way:
We first select an ( X , Y ) vector from the gather indices array using G . The element in the output array at index [ G , O 0 , O 1 ] is then the element in the input array at index [ X + O 0 , Y + O 1 ].
slice_sizes is [8,6] , which decides the range of O 0 and O 1 , and this in turn decides the bounds of the slice.
This gather operation acts as a batch dynamic slice with G as the batch dimension.
The gather indices may be multidimensional. For instance, a more general version of the example above using a "gather indices" array of shape [4,5,2] would translate indices like this:
Again, this acts as a batch dynamic slice G 0 and G 1 as the batch dimensions. The slice size is still [8,6] .
The gather operation in XLA generalizes the informal semantics outlined above in the following ways:
We can configure which dimensions in the output shape are the offset dimensions (dimensions containing
O0,O1in the last example). The output batch dimensions (dimensions containingG0,G1in the last example) are defined to be the output dimensions that are not offset dimensions.The number of output offset dimensions explicitly present in the output shape may be smaller than the input number of dimensions. These "missing" dimensions, which are listed explicitly as
collapsed_slice_dims, must have a slice size of1. Since they have a slice size of1the only valid index for them is0and eliding them does not introduce ambiguity.The slice extracted from the "Gather Indices" array ((
X,Y) in the last example) may have fewer elements than the input array's number of dimensions, and an explicit mapping dictates how the index should be expanded to have the same number of dimensions as the input.
As a final example, we use (2) and (3) to implement tf.gather_nd :
G 0 and G 1 are used to slice out a starting index from the gather indices array as usual, except the starting index has only one element, X . Similarly, there is only one output offset index with the value O 0 . However, before being used as indices into the input array, these are expanded in accordance to "Gather Index Mapping" ( start_index_map in the formal description) and "Offset Mapping" ( remapped_offset_dims in the formal description) into [ X , 0 ] and [ 0 , O 0 ] respectively, adding up to [ X , O 0 ]. In other words, the output index [ G 0 , G 1 , O 0 ] maps to the input index [ GatherIndices [ G 0 , G 1 , 0 ], O 0 ] which gives us the semantics for tf.gather_nd .
slice_sizes for this case is [1,11] . Intuitively this means that every index X in the gather indices array picks an entire row and the result is the concatenation of all these rows.
GetDimensionSize
See also XlaBuilder::GetDimensionSize .
Returns the size of the given dimension of the operand. The operand must be array shaped.
GetDimensionSize(operand, dimension)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | n dimensional input array |
dimension | int64 | A value in the interval [0, n) that specifies the dimension |
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - get_dimension_size .
GetTupleElement
See also XlaBuilder::GetTupleElement .
Indexes into a tuple with a compile-time-constant value.
The value must be a compile-time-constant so that shape inference can determine the type of the resulting value.
This is analogous to std::get<int N>(t) in C++. Conceptually:
let v: f32[10] = f32[10]{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
let s: s32 = 5;
let t: (f32[10], s32) = tuple(v, s);
let element_1: s32 = gettupleelement(t, 1); // Inferred shape matches s32.
See also tf.tuple .
GetTupleElement(tuple_data, index)
| Аргумент | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
tuple_data | XlaOP | The tuple |
index | int64 | Index of tuple shape |
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - get_tuple_element .
Изображение
See also XlaBuilder::Imag .
Element-wise imaginary part of a complex (or real) shape. x -> imag(x) . If the operand is a floating point type, returns 0.
Imag(operand)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to the function |
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - imag .
Подача
See also XlaBuilder::Infeed .
Infeed(shape, config)
| Аргумент | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
shape | Shape | Shape of the data read from the Infeed interface. The layout field of the shape must be set to match the layout of the data sent to the device; otherwise its behavior is undefined. |
config | необязательная string | Configuration of the op. |
Reads a single data item from the implicit Infeed streaming interface of the device, interpreting the data as the given shape and its layout, and returns a XlaOp of the data. Multiple Infeed operations are allowed in a computation, but there must be a total order among the Infeed operations. For example, two Infeed 's in the code below have a total order since there is a dependency between the while loops.
result1 = while (condition, init = init_value) {
Infeed(shape)
}
result2 = while (condition, init = result1) {
Infeed(shape)
}
Nested tuple shapes are not supported. For an empty tuple shape, the Infeed operation is effectively a no-op and proceeds without reading any data from the Infeed of the device.
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - infeed .
Йота
See also XlaBuilder::Iota .
Iota(shape, iota_dimension)
Builds a constant literal on device rather than a potentially large host transfer. Creates an array that has specified shape and holds values starting at zero and incrementing by one along the specified dimension. For floating-point types, the produced array is equivalent to ConvertElementType(Iota(...)) where the Iota is of integral type and the conversion is to the floating-point type.
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
shape | Shape | Shape of the array created by Iota() |
iota_dimension | int64 | The dimension to increment along. |
For example, Iota(s32[4, 8], 0) returns
[[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 ],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 ],
[2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2 ],
[3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3 ]]
Iota(s32[4, 8], 1) returns
[[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 ],
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 ],
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 ],
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 ]]
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - iota .
IsFinite
See also XlaBuilder::IsFinite .
Tests whether each element of operand is finite, ie, is not positive or negative infinity, and is not NaN . Returns an array of PRED values with the same shape as the input, where each element is true if and only if the corresponding input element is finite.
IsFinite(operand)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to the function |
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - is_finite .
Бревно
See also XlaBuilder::Log .
Element-wise natural logarithm x -> ln(x) .
Log(operand)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to the function |
Log also supports the optional result_accuracy argument:
Log(operand, result_accuracy)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to the function |
result_accuracy | optional ResultAccuracy | The types of accuracy the user can request for unary ops with multiple implementations |
For more information on result_accuracy see Result Accuracy .
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - log .
Log1p
See also XlaBuilder::Log1p .
Element-wise shifted natural logarithm x -> ln(1+x) .
Log1p(operand)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to the function |
Log1p also supports the optional result_accuracy argument:
Log1p(operand, result_accuracy)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to the function |
result_accuracy | optional ResultAccuracy | The types of accuracy the user can request for unary ops with multiple implementations |
For more information on result_accuracy see Result Accuracy .
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - log_plus_one .
Логистика
See also XlaBuilder::Logistic .
Element-wise logistic function computation x -> logistic(x) .
Logistic(operand)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to the function |
Logistic also supports the optional result_accuracy argument:
Logistic(operand, result_accuracy)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to the function |
result_accuracy | optional ResultAccuracy | The types of accuracy the user can request for unary ops with multiple implementations |
For more information on result_accuracy see Result Accuracy .
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - logistic .
Карта
See also XlaBuilder::Map .
Map(operands..., computation, dimensions)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operands | sequence of N XlaOp s | N arrays of types T 0..T {N-1} |
computation | XlaComputation | Computation of type T_0, T_1, .., T_{N + M -1} -> S with N parameters of type T and M of arbitrary type. |
dimensions | int64 array | Array of map dimensions |
static_operands | sequence of N XlaOp s | Static ops for the map operation |
Applies a scalar function over the given operands arrays, producing an array of the same dimensions where each element is the result of the mapped function applied to the corresponding elements in the input arrays.
The mapped function is an arbitrary computation with the restriction that it has N inputs of scalar type T and a single output with type S . The output has the same dimensions as the operands except that the element type T is replaced with S.
For example: Map(op1, op2, op3, computation, par1) maps elem_out <- computation(elem1, elem2, elem3, par1) at each (multi-dimensional) index in the input arrays to produce the output array.
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - map .
Макс
See also XlaBuilder::Max .
Performs element-wise max operation on tensors lhs and rhs .
Max(lhs, rhs)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
The arguments' shapes have to be either similar or compatible. See the broadcasting documentation about what it means for shapes to be compatible. The result of an operation has a shape which is the result of broadcasting the two input arrays. In this variant, operations between arrays of different ranks are not supported, unless one of the operands is a scalar.
An alternative variant with different-dimensional broadcasting support exists for Max:
Max(lhs,rhs, broadcast_dimensions)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| broadcast_dimension | ArraySlice | Which dimension in the target shape each dimension of the operand shape corresponds to |
This variant of the operation should be used for arithmetic operations between arrays of different ranks (such as adding a matrix to a vector).
The additional broadcast_dimensions operand is a slice of integers specifying the dimensions to use for broadcasting the operands. The semantics are described in detail on the broadcasting page .
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - maximum .
Мин
See also XlaBuilder::Min .
Performs element-wise min operation on lhs and rhs .
Min(lhs, rhs)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
The arguments' shapes have to be either similar or compatible. See the broadcasting documentation about what it means for shapes to be compatible. The result of an operation has a shape which is the result of broadcasting the two input arrays. In this variant, operations between arrays of different ranks are not supported, unless one of the operands is a scalar.
An alternative variant with different-dimensional broadcasting support exists for Min:
Min(lhs,rhs, broadcast_dimensions)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| broadcast_dimension | ArraySlice | Which dimension in the target shape each dimension of the operand shape corresponds to |
This variant of the operation should be used for arithmetic operations between arrays of different ranks (such as adding a matrix to a vector).
The additional broadcast_dimensions operand is a slice of integers specifying the dimensions to use for broadcasting the operands. The semantics are described in detail on the broadcasting page .
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - minimum .
Мул
See also XlaBuilder::Mul .
Performs element-wise product of lhs and rhs .
Mul(lhs, rhs)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
The arguments' shapes have to be either similar or compatible. See the broadcasting documentation about what it means for shapes to be compatible. The result of an operation has a shape which is the result of broadcasting the two input arrays. In this variant, operations between arrays of different ranks are not supported, unless one of the operands is a scalar.
An alternative variant with different-dimensional broadcasting support exists for Mul:
Mul(lhs,rhs, broadcast_dimensions)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| broadcast_dimension | ArraySlice | Which dimension in the target shape each dimension of the operand shape corresponds to |
This variant of the operation should be used for arithmetic operations between arrays of different ranks (such as adding a matrix to a vector).
The additional broadcast_dimensions operand is a slice of integers specifying the dimensions to use for broadcasting the operands. The semantics are described in detail on the broadcasting page .
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - multiply .
Отрицательный
See also XlaBuilder::Neg .
Element-wise negation x -> -x .
Neg(operand)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to the function |
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - negate
Нет
See also XlaBuilder::Not .
Element-wise logical not x -> !(x) .
Not(operand)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to the function |
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - not .
OptimizationBarrier
See also XlaBuilder::OptimizationBarrier .
Blocks any optimization pass from moving computations across the barrier.
OptimizationBarrier(operand)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to the function |
Ensures that all inputs are evaluated before any operators that depend on the barrier's outputs.
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - optimization_barrier .
Или
See also XlaBuilder::Or .
Performs element-wise OR of lhs and rhs .
Or(lhs, rhs)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
The arguments' shapes have to be either similar or compatible. See the broadcasting documentation about what it means for shapes to be compatible. The result of an operation has a shape which is the result of broadcasting the two input arrays. In this variant, operations between arrays of different ranks are not supported, unless one of the operands is a scalar.
An alternative variant with different-dimensional broadcasting support exists for Or:
Or(lhs,rhs, broadcast_dimensions)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| broadcast_dimension | ArraySlice | Which dimension in the target shape each dimension of the operand shape corresponds to |
This variant of the operation should be used for arithmetic operations between arrays of different ranks (such as adding a matrix to a vector).
The additional broadcast_dimensions operand is a slice of integers specifying the dimensions to use for broadcasting the operands. The semantics are described in detail on the broadcasting page .
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - or .
Outfeed
See also XlaBuilder::Outfeed .
Writes inputs to the outfeed.
Outfeed(operand, shape_with_layout, outfeed_config)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | array of type T |
shape_with_layout | Shape | Defines the layout of the data transferred |
outfeed_config | string | Constant of config for the Outfeed instruction |
shape_with_layout communicates the laid out shape that we want to outfeed.
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - outfeed .
Пад
See also XlaBuilder::Pad .
Pad(operand, padding_value, padding_config)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | array of type T |
padding_value | XlaOp | scalar of type T to fill in the added padding |
padding_config | PaddingConfig | padding amount on both edges (low, high) and between the elements of each dimension |
Expands the given operand array by padding around the array as well as between the elements of the array with the given padding_value . padding_config specifies the amount of edge padding and the interior padding for each dimension.
PaddingConfig is a repeated field of PaddingConfigDimension , which contains three fields for each dimension: edge_padding_low , edge_padding_high , and interior_padding .
edge_padding_low and edge_padding_high specify the amount of padding added at the low-end (next to index 0) and the high-end (next to the highest index) of each dimension respectively. The amount of edge padding can be negative -- the absolute value of negative padding indicates the number of elements to remove from the specified dimension.
interior_padding specifies the amount of padding added between any two elements in each dimension; it may not be negative. Interior padding occurs logically before edge padding, so in the case of negative edge padding, elements are removed from the interior-padded operand.
This operation is a no-op if the edge padding pairs are all (0, 0) and the interior padding values are all 0. The figure below shows examples of different edge_padding and interior_padding values for a two-dimensional array.
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - pad .
Параметр
See also XlaBuilder::Parameter .
Parameter represents an argument input to a computation.
PartitionID
See also XlaBuilder::BuildPartitionId .
Produces partition_id of the current process.
PartitionID(shape)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
shape | Shape | Shape of the data |
PartitionID may appear in HLO dumps but it is not intended to be constructed manually by end users.
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - partition_id .
PopulationCount
See also XlaBuilder::PopulationCount .
Computes the number of bits set in each element of operand .
PopulationCount(operand)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to the function |
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - popcnt .
Поу
See also XlaBuilder::Pow .
Performs element-wise exponentiation of lhs by rhs .
Pow(lhs, rhs)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
The arguments' shapes have to be either similar or compatible. See the broadcasting documentation about what it means for shapes to be compatible. The result of an operation has a shape which is the result of broadcasting the two input arrays. In this variant, operations between arrays of different ranks are not supported, unless one of the operands is a scalar.
An alternative variant with different-dimensional broadcasting support exists for Pow:
Pow(lhs,rhs, broadcast_dimensions)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| broadcast_dimension | ArraySlice | Which dimension in the target shape each dimension of the operand shape corresponds to |
This variant of the operation should be used for arithmetic operations between arrays of different ranks (such as adding a matrix to a vector).
The additional broadcast_dimensions operand is a slice of integers specifying the dimensions to use for broadcasting the operands. The semantics are described in detail on the broadcasting page .
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - power .
Настоящий
See also XlaBuilder::Real .
Element-wise real part of a complex (or real) shape. x -> real(x) . If the operand is a floating point type, Real returns the same value.
Real(operand)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to the function |
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - real .
Получено
See also XlaBuilder::Recv .
Recv , RecvWithTokens , and RecvToHost are operations that serve as communication primitives in HLO. These ops typically appear in HLO dumps as part of low-level input/output or cross-device transfer, but they are not intended to be constructed manually by end users.
Recv(shape, handle)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
shape | Shape | shape of the data to receive |
handle | ChannelHandle | unique identifier for each send/recv pair |
Receives data of the given shape from a Send instruction in another computation that shares the same channel handle. Returns a XlaOp for the received data.
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - recv .
RecvDone
See also HloInstruction::CreateRecv and HloInstruction::CreateRecvDone .
Similar to Send , the client API of Recv operation represents synchronous communication. However, the instruction is internally decomposed into 2 HLO instructions ( Recv and RecvDone ) to enable asynchronous data transfers.
Recv(const Shape& shape, int64 channel_id)
Allocates resources required to receive data from a Send instruction with the same channel_id. Returns a context for the allocated resources, which is used by a following RecvDone instruction to wait for the completion of the data transfer. The context is a tuple of {receive buffer (shape), request identifier (U32)} and it can only be used by a RecvDone instruction.
Given a context created by a Recv instruction, waits for the data transfer to complete and return the received data.
Уменьшать
See also XlaBuilder::Reduce .
Applies a reduction function to one or more arrays in parallel.
Reduce(operands..., init_values..., computation, dimensions_to_reduce)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operands | Sequence of N XlaOp | N arrays of types T_0,..., T_{N-1} . |
init_values | Sequence of N XlaOp | N scalars of types T_0,..., T_{N-1} . |
computation | XlaComputation | computation of type T_0,..., T_{N-1}, T_0, ...,T_{N-1} -> Collate(T_0,..., T_{N-1}) . |
dimensions_to_reduce | int64 array | unordered array of dimensions to reduce. |
Где:
- N is required to be greater or equal to 1.
- The computation has to be "roughly" associative (see below).
- All input arrays must have the same dimensions.
- All initial values have to form an identity under
computation. - If
N = 1,Collate(T)isT. - If
N > 1,Collate(T_0, ..., T_{N-1})is a tuple ofNelements of typeT.
This operation reduces one or more dimensions of each input array into scalars. The number of dimensions of each returned array is number_of_dimensions(operand) - len(dimensions) . The output of the op is Collate(Q_0, ..., Q_N) where Q_i is an array of type T_i , the dimensions of which are described below.
Different backends are allowed to reassociate the reduction computation. This can lead to numerical differences, as some reduction functions like addition are not associative for floats. However, if the range of the data is limited, floating-point addition is close enough to be associative for most practical uses.
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - reduce .
Примеры
When reducing across one dimension in a single 1D array with values [10, 11, 12, 13] , with reduction function f (this is computation ) then that could be computed as
f(10, f(11, f(12, f(init_value, 13)))
but there are also many other possibilities, eg
f(init_value, f(f(10, f(init_value, 11)), f(f(init_value, 12), f(init_value, 13))))
The following is a rough pseudo-code example of how reduction could be implemented, using summation as the reduction computation with an initial value of 0.
result_shape <- remove all dims in dimensions from operand_shape
# Iterate over all elements in result_shape. The number of r's here is equal
# to the number of dimensions of the result.
for r0 in range(result_shape[0]), r1 in range(result_shape[1]), ...:
# Initialize this result element
result[r0, r1...] <- 0
# Iterate over all the reduction dimensions
for d0 in range(dimensions[0]), d1 in range(dimensions[1]), ...:
# Increment the result element with the value of the operand's element.
# The index of the operand's element is constructed from all ri's and di's
# in the right order (by construction ri's and di's together index over the
# whole operand shape).
result[r0, r1...] += operand[ri... di]
Here's an example of reducing a 2D array (matrix). The shape has 2 dimensions, dimension 0 of size 2 and dimension 1 of size 3:
Results of reducing dimensions 0 or 1 with an "add" function:
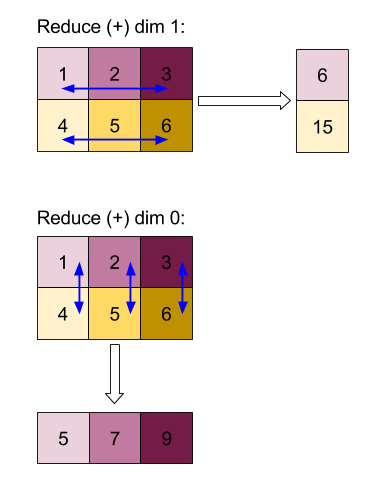
Note that both reduction results are 1D arrays. The diagram shows one as column and another as row just for visual convenience.
For a more complex example, here is a 3D array. Its number of dimensions is 3, dimension 0 of size 4, dimension 1 of size 2 and dimension 2 of size 3. For simplicity, the values 1 to 6 are replicated across dimension 0.
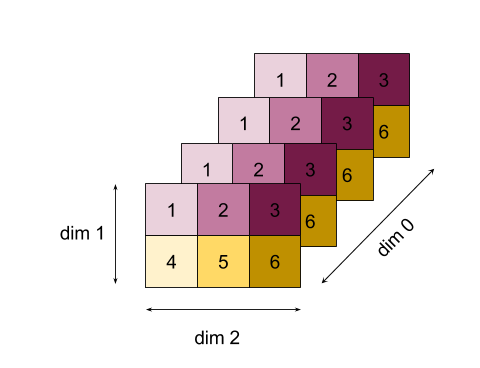
Similarly to the 2D example, we can reduce just one dimension. If we reduce dimension 0, for example, we get a 2-dimensional array where all values across dimension 0 were folded into a scalar:
| 4 8 12 |
| 16 20 24 |
If we reduce dimension 2, we also get a 2-dimensional array where all values across dimension 2 were folded into a scalar:
| 6 15 |
| 6 15 |
| 6 15 |
| 6 15 |
Note that the relative order between the remaining dimensions in the input is preserved in the output, but some dimensions may get assigned new numbers (since the number of dimensions changes).
We can also reduce multiple dimensions. Add-reducing dimensions 0 and 1 produces the 1D array [20, 28, 36] .
Reducing the 3D array over all its dimensions produces the scalar 84 .
Variadic Reduce
When N > 1 , reduce function application is slightly more complex, as it is applied simultaneously to all inputs. The operands are supplied to the computation in the following order:
- Running reduced value for the first operand
- ...
- Running reduced value for the N'th operand
- Input value for the first operand
- ...
- Input value for the N'th operand
For example, consider the following reduction function, which can be used to compute the max and the argmax of a 1-D array in parallel:
f: (Float, Int, Float, Int) -> Float, Int
f(max, argmax, value, index):
if value >= max:
return (value, index)
else:
return (max, argmax)
For 1-D Input arrays V = Float[N], K = Int[N] , and init values I_V = Float, I_K = Int , the result f_(N-1) of reducing across the only input dimension is equivalent to the following recursive application:
f_0 = f(I_V, I_K, V_0, K_0)
f_1 = f(f_0.first, f_0.second, V_1, K_1)
...
f_(N-1) = f(f_(N-2).first, f_(N-2).second, V_(N-1), K_(N-1))
Applying this reduction to an array of values, and an array of sequential indices (ie iota), will co-iterate over the arrays, and return a tuple containing the maximal value and the matching index.
ReducePrecision
See also XlaBuilder::ReducePrecision .
Models the effect of converting floating-point values to a lower-precision format (such as IEEE-FP16) and back to the original format. The number of exponent and mantissa bits in the lower-precision format can be specified arbitrarily, although all bit sizes may not be supported on all hardware implementations.
ReducePrecision(operand, exponent_bits, mantissa_bits)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | array of floating-point type T . |
exponent_bits | int32 | number of exponent bits in lower-precision format |
mantissa_bits | int32 | number of mantissa bits in lower-precision format |
The result is an array of type T . The input values are rounded to the nearest value representable with the given number of mantissa bits (using "ties to even" semantics), and any values that exceed the range specified by the number of exponent bits are clamped to positive or negative infinity. NaN values are retained, although they may be converted to canonical NaN values.
The lower-precision format must have at least one exponent bit (in order to distinguish a zero value from an infinity, since both have a zero mantissa), and must have a non-negative number of mantissa bits. The number of exponent or mantissa bits may exceed the corresponding value for type T ; the corresponding portion of the conversion is then simply a no-op.
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - reduce_precision .
ReduceScatter
See also XlaBuilder::ReduceScatter .
ReduceScatter is a collective operation that effectively does an AllReduce and then scatters the result by splitting it into shard_count blocks along the scatter_dimension and replica i in the replica group receives the ith shard.
ReduceScatter(operand, computation, scatter_dimension, shard_count, replica_groups, channel_id, layout, use_global_device_ids)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | Array or a non-empty tuple of arrays to reduce across replicas. |
computation | XlaComputation | Reduction computation |
scatter_dimension | int64 | Dimension to scatter. |
shard_count | int64 | Number of blocks to split scatter_dimension |
replica_groups | ReplicaGroup vector | Groups between which the reductions are performed |
channel_id | optional ChannelHandle | Optional channel ID for cross-module communication |
layout | optional Layout | user-specified memory layout |
use_global_device_ids | optional bool | user-specified flag |
- When
operandis a tuple of arrays, the reduce-scatter is performed on each element of the tuple. -
replica_groupsis a list of replica groups between which the reduction is performed (replica id for the current replica can be retrieved usingReplicaId). The order of replicas in each group determines the order in which the all-reduce result will be scattered.replica_groupsmust either be empty (in which case all replicas belong to a single group), or contain the same number of elements as the number of replicas. When there are more than one replica groups, they all must be of the same size. For example,replica_groups = {0, 2}, {1, 3}performs reduction between the replicas0and2, and1and3and then scatters the result. -
shard_countis the size of each replica group. We need this in cases wherereplica_groupsare empty. Ifreplica_groupsis not empty,shard_countmust be equal to the size of each replica group. -
channel_idis used for cross-module communication: onlyreduce-scatteroperations with the samechannel_idcan communicate with each other. -
layoutSee xla::shapes for more information on layouts. -
use_global_device_idsis a user-specified flag. Whenfalse(default) the numbers inreplica_groupsareReplicaIdwhentruethereplica_groupsrepresent a global id of (ReplicaID*partition_count+partition_id). For example:- With 2 replicas and 4 partitions,
- replica_groups={ {0,1,4,5},{2,3,6,7} } and use_global_device_ids=true
- group[0] = (0,0), (0,1), (1,0), (1,1)
- group[1] = (0,2), (0,3), (1,2), (1,3)
- where each pair is (replica_id, partition_id).
The output shape is the input shape with the scatter_dimension made shard_count times smaller. For example, if there are two replicas and the operand has the value [1.0, 2.25] and [3.0, 5.25] respectively on the two replicas, then the output value from this op where scatter_dim is 0 will be [4.0] for the first replica and [7.5] for the second replica.
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - reduce_scatter .
ReduceScatter - Example 1 - StableHLO
In the above example, there are 2 replicas participating in the ReduceScatter. On each replica, the operand has shape f32[2,4]. An all-reduce (sum) is performed across the replicas, producing a reduced value of shape f32[2,4] on each replica. This reduced value is then split into 2 parts along dimension 1, so each part has shape f32[2,2]. Each replica within the process group receives the part corresponding to its position in the group. As a result, the output on each replica has shape f32[2,2].
ReduceWindow
See also XlaBuilder::ReduceWindow .
Applies a reduction function to all elements in each window of a sequence of N multi-dimensional arrays, producing a single or a tuple of N multi-dimensional arrays as output. Each output array has the same number of elements as the number of valid positions of the window. A pooling layer can be expressed as a ReduceWindow . Similar to Reduce , the applied computation is always passed the init_values on the left-hand side.
ReduceWindow(operands..., init_values..., computation, window_dimensions, window_strides, padding)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operands | N XlaOps | A sequence of N multi-dimensional arrays of types T_0,..., T_{N-1} , each representing the base area on which the window is placed. |
init_values | N XlaOps | The N starting values for the reduction, one for each of the N operands. See Reduce for details. |
computation | XlaComputation | Reduction function of type T_0, ..., T_{N-1}, T_0, ..., T_{N-1} -> Collate(T_0, ..., T_{N-1}) , to apply to elements in each window of all the input operands. |
window_dimensions | ArraySlice<int64> | array of integers for window dimension values |
window_strides | ArraySlice<int64> | array of integers for window stride values |
base_dilations | ArraySlice<int64> | array of integers for base dilation values |
window_dilations | ArraySlice<int64> | array of integers for window dilation values |
padding | Padding | padding type for window (Padding::kSame, which pads so as to have the same output shape as input if the stride is 1, or Padding::kValid, which uses no padding and "stops" the window once it no longer fits) |
Где:
- N is required to be greater or equal to 1.
- All input arrays must have the same dimensions.
- If
N = 1,Collate(T)isT. - If
N > 1,Collate(T_0, ..., T_{N-1})is a tuple ofNelements of type(T0,...T{N-1}).
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - reduce_window .
ReduceWindow - Example 1
Input is a matrix of size [4x6] and both window_dimensions and window_stride_dimensions are [2x3].
// Create a computation for the reduction (maximum).
XlaComputation max;
{
XlaBuilder builder(client_, "max");
auto y = builder.Parameter(0, ShapeUtil::MakeShape(F32, {}), "y");
auto x = builder.Parameter(1, ShapeUtil::MakeShape(F32, {}), "x");
builder.Max(y, x);
max = builder.Build().value();
}
// Create a ReduceWindow computation with the max reduction computation.
XlaBuilder builder(client_, "reduce_window_2x3");
auto shape = ShapeUtil::MakeShape(F32, {4, 6});
auto input = builder.Parameter(0, shape, "input");
builder.ReduceWindow(
input,
/*init_val=*/builder.ConstantLiteral(LiteralUtil::MinValue(F32)),
*max,
/*window_dimensions=*/{2, 3},
/*window_stride_dimensions=*/{2, 3},
Padding::kValid);
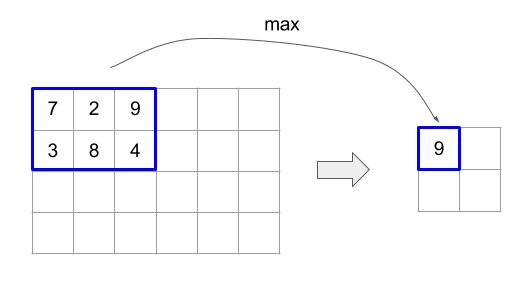
Stride of 1 in a dimension specifies that the position of a window in the dimension is 1 element away from its adjacent window. In order to specify that no windows overlap with each other, window_stride_dimensions should be equal to window_dimensions. The figure below illustrates the use of two different stride values. Padding is applied to each dimension of the input and the calculations are the same as though the input came in with the dimensions it has after padding.
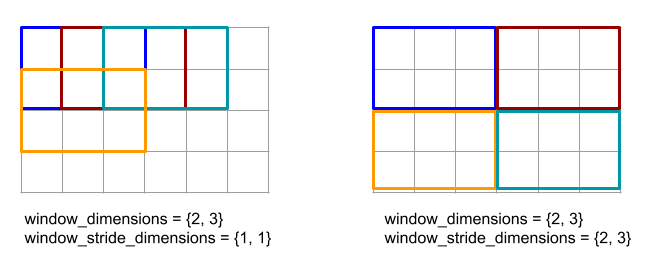
For a non-trivial padding example, consider computing reduce-window minimum (initial value is MAX_FLOAT ) with dimension 3 and stride 2 over the input array [10000, 1000, 100, 10, 1] . Padding kValid computes minimums over two valid windows: [10000, 1000, 100] and [100, 10, 1] , resulting in the output [100, 1] . Padding kSame first pads the array so that the shape after the reduce-window would be the same as input for stride one by adding initial elements on both sides, getting [MAX_VALUE, 10000, 1000, 100, 10, 1, MAX_VALUE] . Running reduce-window over the padded array operates on three windows [MAX_VALUE, 10000, 1000] , [1000, 100, 10] , [10, 1, MAX_VALUE] , and yields [1000, 10, 1] .
The evaluation order of the reduction function is arbitrary and may be non-deterministic. Therefore, the reduction function should not be overly sensitive to reassociation. See the discussion about associativity in the context of Reduce for more details.
ReduceWindow - Example 2 - StableHLO
В приведенном выше примере:
Input) The operand has an input shape of S32[3,2]. With a values of [[1,2],[3,4],[5,6]]
Step 1) Base dilation with factor 2 along the row dimension inserts holes between each row of the operand. Padding of 2 rows at the top and 1 row at the bottom is applied after dilation. As a result, the tensor becomes taller.
Step 2) A window of shape [2,1] is defined, with window dilation [3,1]. This means each window selects two elements from the same column, but the second element is taken three rows below the first rather than directly beneath it.
Step 3) The windows are then slid across the operand with stride [4,1]. This causes the window to move down four rows at a time, while shifting one column at a time horizontally. Padding cells are filled with the init_value (in this case init_value = 0 ). Values 'falling into' dilation cells are ignored. Because of the stride and padding, some windows overlap only zeros and holes, while others overlap real input values.
Step 4) Within each window, the elements are combined using the reduction function (a, b) → a + b, starting from an initial value of 0. The top two windows see only padding and holes, so their results are 0. The bottom windows capture the values 3 and 4 from the input and return those as results.
Results) The final output has shape S32[2,2], with values: [[0,0],[3,4]]
Рем
See also XlaBuilder::Rem .
Performs element-wise remainder of dividend lhs and divisor rhs .
The sign of the result is taken from the dividend, and the absolute value of the result is always less than the divisor's absolute value.
Rem(lhs, rhs)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
The arguments' shapes have to be either similar or compatible. See the broadcasting documentation about what it means for shapes to be compatible. The result of an operation has a shape which is the result of broadcasting the two input arrays. In this variant, operations between arrays of different ranks are not supported, unless one of the operands is a scalar.
An alternative variant with different-dimensional broadcasting support exists for Rem:
Rem(lhs,rhs, broadcast_dimensions)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| broadcast_dimension | ArraySlice | Which dimension in the target shape each dimension of the operand shape corresponds to |
This variant of the operation should be used for arithmetic operations between arrays of different ranks (such as adding a matrix to a vector).
The additional broadcast_dimensions operand is a slice of integers specifying the dimensions to use for broadcasting the operands. The semantics are described in detail on the broadcasting page .
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - remainder .
ReplicaId
See also XlaBuilder::ReplicaId .
Returns the unique ID (U32 scalar) of the replica.
ReplicaId()
The unique ID of each replica is an unsigned integer in the interval [0, N) , where N is the number of replicas. Since all the replicas are running the same program, a ReplicaId() call in the program will return a different value on each replica.
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - replica_id .
Изменить форму
See also XlaBuilder::Reshape . and the Collapse operation.
Reshapes the dimensions of an array into a new configuration.
Reshape(operand, dimensions)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | array of type T |
dimensions | int64 vector | vector of sizes of new dimensions |
Conceptually, reshape first flattens an array into a one-dimensional vector of data values, and then refines this vector into a new shape. The input arguments are an arbitrary array of type T, a compile-time-constant vector of dimension indices, and a compile-time-constant vector of dimension sizes for the result. The dimensions vector determines the size of the output array. The value at index 0 in dimensions is the size of dimension 0, the value at index 1 is the size of dimension 1, and so on. The product of the dimensions dimensions must equal the product of the operand's dimension sizes. When refining the collapsed array into the multidimensional array defined by dimensions , the dimensions in dimensions are ordered from slowest varying (most major) and to fastest varying (most minor).
For example, let v be an array of 24 elements:
let v = f32[4x2x3] { { {10, 11, 12}, {15, 16, 17} },
{ {20, 21, 22}, {25, 26, 27} },
{ {30, 31, 32}, {35, 36, 37} },
{ {40, 41, 42}, {45, 46, 47} } };
let v012_24 = Reshape(v, {24});
then v012_24 == f32[24] {10, 11, 12, 15, 16, 17, 20, 21, 22, 25, 26, 27,
30, 31, 32, 35, 36, 37, 40, 41, 42, 45, 46, 47};
let v012_83 = Reshape(v, {8,3});
then v012_83 == f32[8x3] { {10, 11, 12}, {15, 16, 17},
{20, 21, 22}, {25, 26, 27},
{30, 31, 32}, {35, 36, 37},
{40, 41, 42}, {45, 46, 47} };
As a special case, reshape can transform a single-element array to a scalar and vice versa. For example,
Reshape(f32[1x1] { {5} }, {}) == 5;
Reshape(5, {1,1}) == f32[1x1] { {5} };
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - reshape .
Reshape (explicit)
See also XlaBuilder::Reshape .
Reshape(shape, operand)
Reshape op that uses an explicit target shape.
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
shape | Shape | Output shape of type T |
operand | XlaOp | array of type T |
Rev (reverse)
See also XlaBuilder::Rev .
Rev(operand, dimensions)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | array of type T |
dimensions | ArraySlice<int64> | dimensions to reverse |
Reverses the order of elements in the operand array along the specified dimensions , generating an output array of the same shape. Each element of the operand array at a multidimensional index is stored into the output array at a transformed index. The multidimensional index is transformed by reversing the index in each dimension to be reversed (ie, if a dimension of size N is one of the reversing dimensions, its index i is transformed into N - 1 - i).
One use for the Rev operation is to reverse the convolution weight array along the two window dimensions during the gradient computation in neural networks.
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - reverse .
RngNormal
See also XlaBuilder::RngNormal .
Constructs an output of a given shape with random numbers generated following the \(N(\mu, \sigma)\) normal distribution. The parameters \(\mu\) и \(\sigma\), and output shape have to have a floating point elemental type. The parameters furthermore have to be scalar valued.
RngNormal(mu, sigma, shape)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
mu | XlaOp | Scalar of type T specifying mean of generated numbers |
sigma | XlaOp | Scalar of type T specifying standard deviation of generated |
shape | Shape | Output shape of type T |
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - rng .
RngUniform
See also XlaBuilder::RngUniform .
Constructs an output of a given shape with random numbers generated following the uniform distribution over the interval \([a,b)\). The parameters and output element type have to be a boolean type, an integral type or a floating point types, and the types have to be consistent. The CPU and GPU backends currently only support F64, F32, F16, BF16, S64, U64, S32 and U32. Furthermore, the parameters need to be scalar valued. If \(b <= a\) the result is implementation-defined.
RngUniform(a, b, shape)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
a | XlaOp | Scalar of type T specifying lower limit of interval |
b | XlaOp | Scalar of type T specifying upper limit of interval |
shape | Shape | Output shape of type T |
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - rng .
RngBitGenerator
See also XlaBuilder::RngBitGenerator .
Generates an output with a given shape filled with uniform random bits using the specified algorithm (or backend default) and returns an updated state (with the same shape as initial state) and the generated random data.
Initial state is the initial state of the current random number generation. It and the required shape and valid values are dependent on the algorithm used.
The output is guaranteed to be a deterministic function of the initial state but it is not guaranteed to be deterministic between backends and different compiler versions.
RngBitGenerator(algorithm, initial_state, shape)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
algorithm | RandomAlgorithm | PRNG algorithm to be used. |
initial_state | XlaOp | Initial state for the PRNG algorithm. |
shape | Shape | Output shape for generated data. |
Available values for algorithm :
rng_default: Backend specific algorithm with backend specific shape requirements.rng_three_fry: ThreeFry counter-based PRNG algorithm. Theinitial_stateshape isu64[2]with arbitrary values. Salmon et al. SC 2011. Parallel random numbers: as easy as 1, 2, 3.rng_philox: Philox algorithm to generate random numbers in parallel. Theinitial_stateshape isu64[3]with arbitrary values. Salmon et al. SC 2011. Parallel random numbers: as easy as 1, 2, 3.
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - rng_bit_generator .
RngGetAndUpdateState
See also HloInstruction::CreateRngGetAndUpdateState .
The API of the various Rng operations are internally decomposed into HLO instructions including RngGetAndUpdateState .
RngGetAndUpdateState serves as a primitive in HLO. This op may appear in HLO dumps, but it is not intended to be constructed manually by end users.
Круглый
See also XlaBuilder::Round .
Element-wise rounding, ties away from zero.
Round(operand)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to the function |
RoundNearestAfz
See also XlaBuilder::RoundNearestAfz .
Performs element-wise rounding towards the nearest integer, breaking ties away from zero.
RoundNearestAfz(operand)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to the function |
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - round_nearest_afz .
RoundNearestEven
See also XlaBuilder::RoundNearestEven .
Element-wise rounding, ties to the nearest even.
RoundNearestEven(operand)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to the function |
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - round_nearest_even .
Rsqrt
See also XlaBuilder::Rsqrt .
Element-wise reciprocal of square root operation x -> 1.0 / sqrt(x) .
Rsqrt(operand)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to the function |
Rsqrt also supports the optional result_accuracy argument:
Rsqrt(operand, result_accuracy)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to the function |
result_accuracy | optional ResultAccuracy | The types of accuracy the user can request for unary ops with multiple implementations |
For more information on result_accuracy see Result Accuracy .
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - rsqrt .
Сканировать
See also XlaBuilder::Scan .
Applies a reduction function to an array across a given dimension, producing a final state and an array of intermediate values.
Scan(inputs..., inits..., to_apply, scan_dimension, is_reverse, is_associative)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
inputs | Sequence of m XlaOp s | The arrays to scan. |
inits | Sequence of k XlaOp s | Initial carries. |
to_apply | XlaComputation | Computation of type i_0, ..., i_{m-1}, c_0, ..., c_{k-1} -> (o_0, ..., o_{n-1}, c'_0, ..., c'_{k-1}) . |
scan_dimension | int64 | The dimension to scan across. |
is_reverse | bool | If true, scan in reverse order. |
is_associative | bool (tri-state) | If true, the operation is associative. |
The function to_apply is applied sequentially to elements in inputs along scan_dimension . If is_reverse is false, elements are processed in order 0 to N-1 , where N is the size of scan_dimension . If is_reverse is true, elements are processed from N-1 down to 0 .
The to_apply function takes m + k operands:
-
mcurrent elements frominputs. -
kcarry values from the previous step (orinitsfor the first element).
The to_apply function returns a tuple of n + k values:
-
nelements ofoutputs. -
knew carry values.
The Scan operation produces a tuple of n + k values:
- The
noutput arrays, containing the output values for each step. - The final
kcarry values after processing all elements.
The types of the m inputs must match the types of the first m parameters of to_apply with an extra scan dimension. The types of the n outputs must match the types of the first n return values of to_apply with an extra scan dimension. The extra scan dimension among all inputs and outputs must have the same size N . The types of the last k parameters and return values of to_apply as well as the k inits must match.
For example ( m, n, k == 1, N == 3 ), for initial carry i , input [a, b, c] , function f(x, c) -> (y, c') , and scan_dimension=0 , is_reverse=false :
- Step 0:
f(a, i) -> (y0, c0) - Step 1:
f(b, c0) -> (y1, c1) - Step 2:
f(c, c1) -> (y2, c2)
The output of Scan is ([y0, y1, y2], c2) .
Рассеивание
See also XlaBuilder::Scatter .
The XLA scatter operation generates a sequence of results which are the values of the input array operands , with several slices (at indices specified by scatter_indices ) updated with the sequence of values in updates using update_computation .
Scatter(operands..., scatter_indices, updates..., update_computation, dimension_numbers, indices_are_sorted, unique_indices)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operands | Sequence of N XlaOp | N arrays of types T_0, ..., T_N to be scattered into. |
scatter_indices | XlaOp | Array containing the starting indices of the slices that must be scattered to. |
updates | Sequence of N XlaOp | N arrays of types T_0, ..., T_N . updates[i] contains the values that must be used for scattering operands[i] . |
update_computation | XlaComputation | Computation to be used for combining the existing values in the input array and the updates during scatter. This computation should be of type T_0, ..., T_N, T_0, ..., T_N -> Collate(T_0, ..., T_N) . |
index_vector_dim | int64 | The dimension in scatter_indices that contains the starting indices. |
update_window_dims | ArraySlice<int64> | The set of dimensions in updates shape that are window dimensions . |
inserted_window_dims | ArraySlice<int64> | The set of window dimensions that must be inserted into updates shape. |
scatter_dims_to_operand_dims | ArraySlice<int64> | A dimensions map from the scatter indices to the operand index space. This array is interpreted as mapping i to scatter_dims_to_operand_dims[i] . It has to be one-to-one and total. |
dimension_number | ScatterDimensionNumbers | Dimension numbers for scatter operation |
indices_are_sorted | bool | Whether the indices are guaranteed to be sorted by the caller. |
unique_indices | bool | Whether the indices are guaranteed to be unique by the caller. |
Где:
- N is required to be greater or equal to 1.
-
operands[0], ...,operands[N-1] must all have the same dimensions. -
updates[0], ...,updates[N-1] must all have the same dimensions. - If
N = 1,Collate(T)isT. - If
N > 1,Collate(T_0, ..., T_N)is a tuple ofNelements of typeT.
If index_vector_dim is equal to scatter_indices.rank we implicitly consider scatter_indices to have a trailing 1 dimension.
We define update_scatter_dims of type ArraySlice<int64> as the set of dimensions in updates shape that are not in update_window_dims , in ascending order.
The arguments of scatter should follow these constraints:
Each
updatesarray must haveupdate_window_dims.size + scatter_indices.rank - 1dimensions.Bounds of dimension
iin eachupdatesarray must conform to the following:- If
iis present inupdate_window_dims(ie equal toupdate_window_dims[k] for somek), then the bound of dimensioniinupdatesmust not exceed the corresponding bound ofoperandafter accounting for theinserted_window_dims(ieadjusted_window_bounds[k], whereadjusted_window_boundscontains the bounds ofoperandwith the bounds at indicesinserted_window_dimsremoved). - If
iis present inupdate_scatter_dims(ie equal toupdate_scatter_dims[k] for somek), then the bound of dimensioniinupdatesmust be equal to the corresponding bound ofscatter_indices, skippingindex_vector_dim(iescatter_indices.shape.dims[k], ifk<index_vector_dimandscatter_indices.shape.dims[k+1] otherwise).
- If
update_window_dimsmust be in ascending order, not have any repeating dimension numbers, and be in the range[0, updates.rank).inserted_window_dimsmust be in ascending order, not have any repeating dimension numbers, and be in the range[0, operand.rank).operand.rankmust equal the sum ofupdate_window_dims.sizeandinserted_window_dims.size.scatter_dims_to_operand_dims.sizemust be equal toscatter_indices.shape.dims[index_vector_dim], and its values must be in the range[0, operand.rank).
For a given index U in each updates array, the corresponding index I in the corresponding operands array into which this update has to be applied is computed as follows:
- Let
G= {U[k] forkinupdate_scatter_dims}. UseGto look up an index vectorSin thescatter_indicesarray such thatS[i] =scatter_indices[Combine(G,i)] where Combine(A, b) inserts b at positionsindex_vector_diminto A. - Create an index
SinintooperandusingSby scatteringSusing thescatter_dims_to_operand_dimsmap. More formally:-
Sin[scatter_dims_to_operand_dims[k]] =S[k] ifk<scatter_dims_to_operand_dims.size. -
Sin[_] =0otherwise.
-
- Create an index
Wininto eachoperandsarray by scattering the indices atupdate_window_dimsinUaccording toinserted_window_dims. More formally:-
Win[window_dims_to_operand_dims(k)] =U[k] ifkis inupdate_window_dims, wherewindow_dims_to_operand_dimsis the monotonic function with domain [0,update_window_dims.size) and range [0,operand.rank) \inserted_window_dims. (For example, ifupdate_window_dims.sizeis4,operand.rankis6, andinserted_window_dimsis {0,2} thenwindow_dims_to_operand_dimsis {0→1,1→3,2→4,3→5}). -
Win[_] =0otherwise.
-
-
IisWin+Sinwhere + is element-wise addition.
In summary, the scatter operation can be defined as follows.
- Initialize
outputwithoperands, ie for all indicesJ, for all indicesOin theoperands[J] array:
output[J][O] =operands[J][O] - For every index
Uin theupdates[J] array and the corresponding indexOin theoperand[J] array, ifOis a valid index foroutput:
(output[0][O], ...,output[N-1][O]) =update_computation(output[0][O], ..., ,output[N-1][O],updates[0][U], ...,updates[N-1][U])
The order in which updates are applied is non-deterministic. So, when multiple indices in updates refer to the same index in operands , the corresponding value in output will be non-deterministic.
Note that the first parameter that is passed into the update_computation will always be the current value from the output array and the second parameter will always be the value from the updates array. This is important specifically for cases when the update_computation is not commutative .
If indices_are_sorted is set to true then XLA can assume that scatter_indices are sorted (in ascending order, after scattering its values according to scatter_dims_to_operand_dims ) by the user. If they are not then the semantics are implementation defined.
If unique_indices is set to true then XLA can assume that all elements scattered to are unique. So XLA could use non-atomic operations. If unique_indices is set to true and the indices being scattered to are not unique then the semantics is implementation defined.
Informally, the scatter op can be viewed as an inverse of the gather op, ie the scatter op updates the elements in the input that are extracted by the corresponding gather op.
For a detailed informal description and examples, refer to the "Informal Description" section under Gather .
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - scatter .
Scatter - Example 1 - StableHLO
In the above image, each row of the table is an example of one update index example. Let's review stepwise from left(Update Index) to right(Result Index):
Input) input has shape S32[2,3,4,2]. scatter_indices have shape S64[2,2,3,2]. updates have shape S32[2,2,3,1,2].
Update Index) As part of the input we are given update_window_dims:[3,4] . This tell us that updates 's dim 3 and dim 4 are window dimensions, highlighted in yellow. This allows us to derive that update_scatter_dims = [0,1,2].
Update Scatter Index) Shows us the extracted updated_scatter_dims for each. (The non-yellow of column Update Index)
Start Index) Looking at the scatter_indices tensor image we can see that our values from the previous step (Update scatter Index), give us the location of the start index. From index_vector_dim we are also told the dimension of the starting_indices that contains the starting indices, which for scatter_indices is dim 3 with a size 2.
Full Start Index) scatter_dims_to_operand_dims = [2,1] tells us the first element of the index vector goes to operand dim 2. The second element of the index vector goes to operand dim 1. The remaining operand dimensions are filled with 0.
Full Batching Index) We can see the purple highlighted area is shown in this column(full batching index), the update scatter index column, and update index column.
Full Window Index) Computed from the update_window_dimensions [3,4].
Result Index) The addition of Full Start Index, Full Batching Index, and Full Window Index in the operand tensor. Notice the green highlighted regions correspond to the operand figure as well. The last row is skipped because it falls outside of operand tensor.
Выбирать
See also XlaBuilder::Select .
Constructs an output array from elements of two input arrays, based on the values of a predicate array.
Select(pred, on_true, on_false)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
pred | XlaOp | array of type PRED |
on_true | XlaOp | array of type T |
on_false | XlaOp | array of type T |
The arrays on_true and on_false must have the same shape. This is also the shape of the output array. The array pred must have the same dimensionality as on_true and on_false , with the PRED element type.
For each element P of pred , the corresponding element of the output array is taken from on_true if the value of P is true , and from on_false if the value of P is false . As a restricted form of broadcasting , pred can be a scalar of type PRED . In this case, the output array is taken wholly from on_true if pred is true , and from on_false if pred is false .
Example with non-scalar pred :
let pred: PRED[4] = {true, false, false, true};
let v1: s32[4] = {1, 2, 3, 4};
let v2: s32[4] = {100, 200, 300, 400};
==>
Select(pred, v1, v2) = s32[4]{1, 200, 300, 4};
Example with scalar pred :
let pred: PRED = true;
let v1: s32[4] = {1, 2, 3, 4};
let v2: s32[4] = {100, 200, 300, 400};
==>
Select(pred, v1, v2) = s32[4]{1, 2, 3, 4};
Selections between tuples are supported. Tuples are considered to be scalar types for this purpose. If on_true and on_false are tuples (which must have the same shape!) then pred has to be a scalar of type PRED .
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - select
SelectAndScatter
See also XlaBuilder::SelectAndScatter .
This operation can be considered as a composite operation that first computes ReduceWindow on the operand array to select an element from each window, and then scatters the source array to the indices of the selected elements to construct an output array with the same shape as the operand array. The binary select function is used to select an element from each window by applying it across each window, and it is called with the property that the first parameter's index vector is lexicographically less than the second parameter's index vector. The select function returns true if the first parameter is selected and returns false if the second parameter is selected, and the function must hold transitivity (ie, if select(a, b) and select(b, c) are true , then select(a, c) is also true ) so that the selected element does not depend on the order of the elements traversed for a given window.
The function scatter is applied at each selected index in the output array. It takes two scalar parameters:
- Current value at the selected index in the output array
- The scatter value from
sourcethat applies to the selected index
It combines the two parameters and returns a scalar value that's used to update the value at the selected index in the output array. Initially, all indices of the output array are set to init_value .
The output array has the same shape as the operand array and the source array must have the same shape as the result of applying a ReduceWindow operation on the operand array. SelectAndScatter can be used to backpropagate the gradient values for a pooling layer in a neural network.
SelectAndScatter(operand, select, window_dimensions, window_strides, padding, source, init_value, scatter)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | array of type T over which the windows slide |
select | XlaComputation | binary computation of type T, T -> PRED , to apply to all elements in each window; returns true if the first parameter is selected and returns false if the second parameter is selected |
window_dimensions | ArraySlice<int64> | array of integers for window dimension values |
window_strides | ArraySlice<int64> | array of integers for window stride values |
padding | Padding | padding type for window (Padding::kSame or Padding::kValid) |
source | XlaOp | array of type T with the values to scatter |
init_value | XlaOp | scalar value of type T for the initial value of the output array |
scatter | XlaComputation | binary computation of type T, T -> T , to apply each scatter source element with its destination element |
The figure below shows examples of using SelectAndScatter , with the select function computing the maximal value among its parameters. Note that when the windows overlap, as in the figure (2) below, an index of the operand array may be selected multiple times by different windows. In the figure, the element of value 9 is selected by both of the top windows (blue and red) and the binary addition scatter function produces the output element of value 8 (2 + 6).
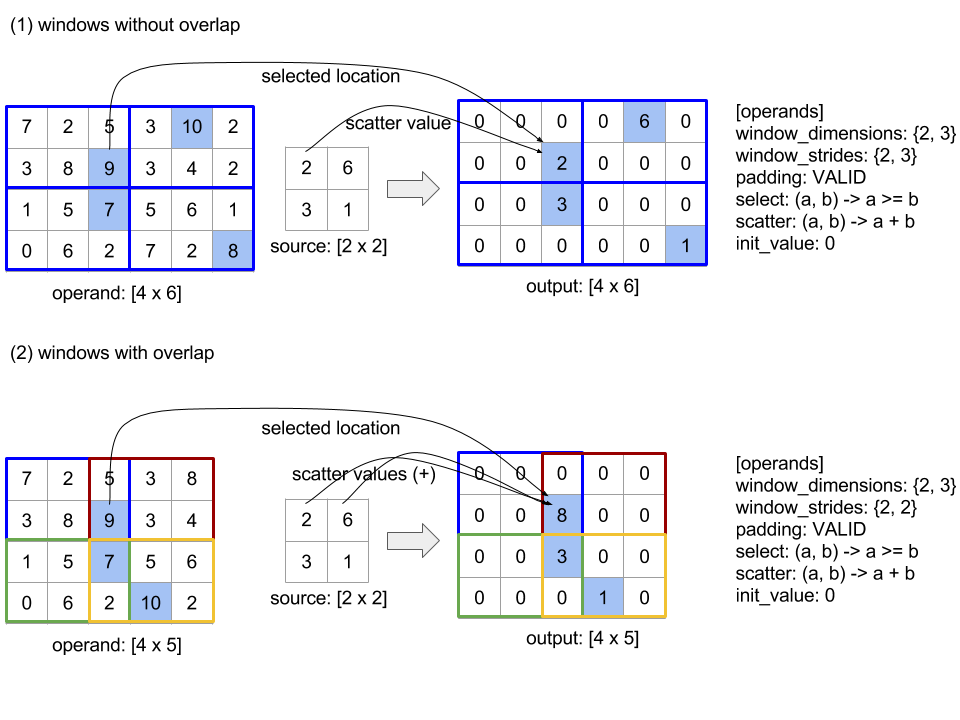
The evaluation order of the scatter function is arbitrary and may be non-deterministic. Therefore, the scatter function should not be overly sensitive to reassociation. See the discussion about associativity in the context of Reduce for more details.
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - select_and_scatter .
Отправлять
See also XlaBuilder::Send .
Send , SendWithTokens , and SendToHost are operations that serve as communication primitives in HLO. These ops typically appear in HLO dumps as part of low-level input/output or cross-device transfer, but they are not intended to be constructed manually by end users.
Send(operand, handle)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | data to send (array of type T) |
handle | ChannelHandle | unique identifier for each send/recv pair |
Sends the given operand data to a Recv instruction in another computation that shares the same channel handle. Does not return any data.
Similar to the Recv operation, the client API of Send operation represents synchronous communication, and is internally decomposed into 2 HLO instructions ( Send and SendDone ) to enable asynchronous data transfers. See also HloInstruction::CreateSend and HloInstruction::CreateSendDone .
Send(HloInstruction operand, int64 channel_id)
Initiates an asynchronous transfer of the operand to the resources allocated by the Recv instruction with the same channel id. Returns a context, which is used by a following SendDone instruction to wait for the completion of the data transfer. The context is a tuple of {operand (shape), request identifier (U32)} and it can only be used by a SendDone instruction.
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - send .
SendDone
See also HloInstruction::CreateSendDone .
SendDone(HloInstruction context)
Given a context created by a Send instruction, waits for the data transfer to complete. The instruction does not return any data.
Scheduling of channel instructions
The execution order of the 4 instructions for each channel ( Recv , RecvDone , Send , SendDone ) is as below.
-
Recvhappens beforeSend -
Sendhappens beforeRecvDone -
Recvhappens beforeRecvDone -
Sendhappens beforeSendDone
When the backend compilers generate a linear schedule for each computation that communicates via channel instructions, there must not be cycles across the computations. For example, below schedules lead to deadlocks.
SetDimensionSize
See also XlaBuilder::SetDimensionSize .
Sets the dynamic size of XlaOp's given dimension. The operand must be array shaped.
SetDimensionSize(operand, val, dimension)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | n dimensional input array. |
val | XlaOp | int32 representing the runtime dynamic size. |
dimension | int64 | A value in the interval [0, n) that specifies the dimension. |
Pass through the operand as result, with dynamic dimension tracked by the compiler.
Padded values will be ignored by downstream reduction ops.
let v: f32[10] = f32[10]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
let five: s32 = 5;
let six: s32 = 6;
// Setting dynamic dimension size doesn't change the upper bound of the static
// shape.
let padded_v_five: f32[10] = set_dimension_size(v, five, /*dimension=*/0);
let padded_v_six: f32[10] = set_dimension_size(v, six, /*dimension=*/0);
// sum == 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5
let sum:f32[] = reduce_sum(padded_v_five);
// product == 1 * 2 * 3 * 4 * 5
let product:f32[] = reduce_product(padded_v_five);
// Changing padding size will yield different result.
// sum == 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6
let sum:f32[] = reduce_sum(padded_v_six);
ShiftLeft
See also XlaBuilder::ShiftLeft .
Performs element-wise left-shift operation on lhs by rhs number of bits.
ShiftLeft(lhs, rhs)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
The arguments' shapes have to be either similar or compatible. See the broadcasting documentation about what it means for shapes to be compatible. The result of an operation has a shape which is the result of broadcasting the two input arrays. In this variant, operations between arrays of different ranks are not supported, unless one of the operands is a scalar.
An alternative variant with different-dimensional broadcasting support exists for ShiftLeft:
ShiftLeft(lhs,rhs, broadcast_dimensions)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| broadcast_dimension | ArraySlice | Which dimension in the target shape each dimension of the operand shape corresponds to |
This variant of the operation should be used for arithmetic operations between arrays of different ranks (such as adding a matrix to a vector).
The additional broadcast_dimensions operand is a slice of integers specifying the dimensions to use for broadcasting the operands. The semantics are described in detail on the broadcasting page .
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - shift_left .
ShiftRightArithmetic
See also XlaBuilder::ShiftRightArithmetic .
Performs element-wise arithmetic right-shift operation on lhs by rhs number of bits.
ShiftRightArithmetic(lhs, rhs)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
The arguments' shapes have to be either similar or compatible. See the broadcasting documentation about what it means for shapes to be compatible. The result of an operation has a shape which is the result of broadcasting the two input arrays. In this variant, operations between arrays of different ranks are not supported, unless one of the operands is a scalar.
An alternative variant with different-dimensional broadcasting support exists for ShiftRightArithmetic:
ShiftRightArithmetic(lhs,rhs, broadcast_dimensions)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| broadcast_dimension | ArraySlice | Which dimension in the target shape each dimension of the operand shape corresponds to |
This variant of the operation should be used for arithmetic operations between arrays of different ranks (such as adding a matrix to a vector).
The additional broadcast_dimensions operand is a slice of integers specifying the dimensions to use for broadcasting the operands. The semantics are described in detail on the broadcasting page .
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - shift_right_arithmetic .
ShiftRightLogical
See also XlaBuilder::ShiftRightLogical .
Performs element-wise logical right-shift operation on lhs by rhs number of bits.
ShiftRightLogical(lhs, rhs)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
The arguments' shapes have to be either similar or compatible. See the broadcasting documentation about what it means for shapes to be compatible. The result of an operation has a shape which is the result of broadcasting the two input arrays. In this variant, operations between arrays of different ranks are not supported, unless one of the operands is a scalar.
An alternative variant with different-dimensional broadcasting support exists for ShiftRightLogical:
ShiftRightLogical(lhs,rhs, broadcast_dimensions)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| broadcast_dimension | ArraySlice | Which dimension in the target shape each dimension of the operand shape corresponds to |
This variant of the operation should be used for arithmetic operations between arrays of different ranks (such as adding a matrix to a vector).
The additional broadcast_dimensions operand is a slice of integers specifying the dimensions to use for broadcasting the operands. The semantics are described in detail on the broadcasting page .
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - shift_right_logical .
Знак
See also XlaBuilder::Sign .
Sign(operand) Element-wise sign operation x -> sgn(x) where
\[\text{sgn}(x) = \begin{cases} -1 & x < 0\\ -0 & x = -0\\ NaN & x = NaN\\ +0 & x = +0\\ 1 & x > 0 \end{cases}\]
using the comparison operator of the element type of operand .
Sign(operand)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to the function |
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - sign .
Грех
Sin(operand) Element-wise sine x -> sin(x) .
See also XlaBuilder::Sin .
Sin(operand)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to the function |
Sin also supports the optional result_accuracy argument:
Sin(operand, result_accuracy)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to the function |
result_accuracy | optional ResultAccuracy | The types of accuracy the user can request for unary ops with multiple implementations |
For more information on result_accuracy see Result Accuracy .
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - sine .
Ломтик
See also XlaBuilder::Slice .
Slicing extracts a sub-array from the input array. The sub-array has the same number of dimensions as the input and contains the values inside a bounding box within the input array where the dimensions and indices of the bounding box are given as arguments to the slice operation.
Slice(operand, start_indices, limit_indices, strides)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | N dimensional array of type T |
start_indices | ArraySlice<int64> | List of N integers containing the starting indices of the slice for each dimension. Values must be greater than or equal to zero. |
limit_indices | ArraySlice<int64> | List of N integers containing the ending indices (exclusive) for the slice for each dimension. Each value must be greater than or equal to the respective start_indices value for the dimension and less than or equal to the size of the dimension. |
strides | ArraySlice<int64> | List of N integers that decides the input stride of the slice. The slice picks every strides[d] element in dimension d . |
1-dimensional example:
let a = {0.0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0}
Slice(a, {2}, {4})
// Result: {2.0, 3.0}
2-dimensional example:
let b =
{ {0.0, 1.0, 2.0},
{3.0, 4.0, 5.0},
{6.0, 7.0, 8.0},
{9.0, 10.0, 11.0} }
Slice(b, {2, 1}, {4, 3})
// Result:
// { { 7.0, 8.0},
// {10.0, 11.0} }
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - slice .
Сортировка
See also XlaBuilder::Sort .
Sort(operands, comparator, dimension, is_stable)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operands | ArraySlice<XlaOp> | The operands to sort. |
comparator | XlaComputation | The comparator computation to use. |
dimension | int64 | The dimension along which to sort. |
is_stable | bool | Whether stable sorting should be used. |
If only one operand is provided:
If the operand is a 1-dimensional tensor (an array), the result is a sorted array. If you want to sort the array into ascending order, the comparator should perform a less-than comparison. Formally, after the array is sorted, it holds for all index positions
i, jwithi < jthat eithercomparator(value[i], value[j]) = comparator(value[j], value[i]) = falseorcomparator(value[i], value[j]) = true.If the operand has higher number of dimensions, the operand is sorted along the provided dimension. For example, for a 2-dimensional tensor (a matrix), a dimension value of
0will independently sort every column, and a dimension value of1will independently sort each row. If no dimension number is provided, then the last dimension is chosen by default. For the dimension which is sorted, the same sorting order applies as in the 1-dimensional case.
If n > 1 operands are provided:
All
noperands must be tensors with the same dimensions. The element types of the tensors may be different.All operands are sorted together, not individually. Conceptually the operands are treated as a tuple. When checking whether the elements of each operand at index positions
iandjneed to be swapped, the comparator is called with2 * nscalar parameters, where parameter2 * kcorresponds to the value at positionifrom thek-thoperand, and parameter2 * k + 1corresponds to the value at positionjfrom thek-thoperand. Usually, the comparator would thus compare parameters2 * kand2 * k + 1with each other and possibly use other parameter pairs as tie breakers.The result is a tuple that consists of the operands in sorted order (along the provided dimension, as above). The
i-thoperand of the tuple corresponds to thei-thoperand of Sort.
For example, if there are three operands operand0 = [3, 1] , operand1 = [42, 50] , operand2 = [-3.0, 1.1] , and the comparator compares only the values of operand0 with less-than, then the output of the sort is the tuple ([1, 3], [50, 42], [1.1, -3.0]) .
If is_stable is set to true, the sort is guaranteed to be stable, that is, if there are elements which are considered to be equal by the comparator, the relative order of the equal values is preserved. Two elements e1 and e2 are equal if and only if comparator(e1, e2) = comparator(e2, e1) = false . By default, is_stable is set to false.
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - sort .
квадратный корень
See also XlaBuilder::Sqrt .
Element-wise square root operation x -> sqrt(x) .
Sqrt(operand)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to the function |
Sqrt also supports the optional result_accuracy argument:
Sqrt(operand, result_accuracy)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to the function |
result_accuracy | optional ResultAccuracy | The types of accuracy the user can request for unary ops with multiple implementations |
For more information on result_accuracy see Result Accuracy .
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - sqrt .
Под
See also XlaBuilder::Sub .
Performs element-wise subtraction of lhs and rhs .
Sub(lhs, rhs)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
The arguments' shapes have to be either similar or compatible. See the broadcasting documentation about what it means for shapes to be compatible. The result of an operation has a shape which is the result of broadcasting the two input arrays. In this variant, operations between arrays of different ranks are not supported, unless one of the operands is a scalar.
An alternative variant with different-dimensional broadcasting support exists for Sub:
Sub(lhs,rhs, broadcast_dimensions)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| broadcast_dimension | ArraySlice | Which dimension in the target shape each dimension of the operand shape corresponds to |
This variant of the operation should be used for arithmetic operations between arrays of different ranks (such as adding a matrix to a vector).
The additional broadcast_dimensions operand is a slice of integers specifying the dimensions to use for broadcasting the operands. The semantics are described in detail on the broadcasting page .
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - subtract .
Загар
See also XlaBuilder::Tan .
Element-wise tangent x -> tan(x) .
Tan(operand)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to the function |
Tan also supports the optional result_accuracy argument:
Tan(operand, result_accuracy)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to the function |
result_accuracy | optional ResultAccuracy | The types of accuracy the user can request for unary ops with multiple implementations |
For more information on result_accuracy see Result Accuracy .
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - tan .
Танх
See also XlaBuilder::Tanh .
Element-wise hyperbolic tangent x -> tanh(x) .
Tanh(operand)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to the function |
Tanh also supports the optional result_accuracy argument:
Tanh(operand, result_accuracy)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to the function |
result_accuracy | optional ResultAccuracy | The types of accuracy the user can request for unary ops with multiple implementations |
For more information on result_accuracy see Result Accuracy .
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - tanh .
ТопК
See also XlaBuilder::TopK .
TopK finds the values and indices of the k largest or smallest elements for the last dimension of the given tensor.
TopK(operand, k, largest)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The tensor from which to extract the top k elements. The tensor must have greater or equal to one dimensions. The size of the last dimension of the tensor must be greater or equal to k . |
k | int64 | The number of elements to extract. |
largest | bool | Whether to extract the largest or smallest k elements. |
For a 1-dimensional input tensor (an array), finds the k largest or smallest entries in the array and outputs a tuple of two arrays (values, indices) . Thus values[j] is the j -th largest/smallest entry in operand , and its index is indices[j] .
For an input tensor with more than 1 dimension, computes the top k entries along the last dimension, preserving all other dimensions (rows) in the output. Thus, for an operand of shape [A, B, ..., P, Q] where Q >= k the output is a tuple (values, indices) where:
values.shape = indices.shape = [A, B, ..., P, k]
If two elements within a row are equal, the lower-index element appears first.
Транспонировать
See also the tf.reshape operation.
Transpose(operand, permutation)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
operand | XlaOp | The operand to transpose. |
permutation | ArraySlice<int64> | How to permute the dimensions. |
Permutes the operand dimensions with the given permutation, so ∀ i . 0 ≤ i < number of dimensions ⇒ input_dimensions[permutation[i]] = output_dimensions[i] .
This is the same as Reshape(operand, permutation, Permute(permutation, operand.shape.dimensions)).
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - transpose .
TriangularSolve
See also XlaBuilder::TriangularSolve .
Solves systems of linear equations with lower or upper triangular coefficient matrices by forward- or back-substitution. Broadcasting along leading dimensions, this routine solves one of the matrix systems op(a) * x = b , or x * op(a) = b , for the variable x , given a and b , where op(a) is either op(a) = a , or op(a) = Transpose(a) , or op(a) = Conj(Transpose(a)) .
TriangularSolve(a, b, left_side, lower, unit_diagonal, transpose_a)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
a | XlaOp | a > 2 dimensional array of a complex or floating-point type with shape [..., M, M] . |
b | XlaOp | a > 2 dimensional array of the same type with shape [..., M, K] if left_side is true, [..., K, M] otherwise. |
left_side | bool | indicates whether to solve a system of the form op(a) * x = b ( true ) or x * op(a) = b ( false ). |
lower | bool | whether to use the upper or lower triangle of a . |
unit_diagonal | bool | if true , the diagonal elements of a are assumed to be 1 and not accessed. |
transpose_a | Transpose | whether to use a as is, transpose it or take its conjugate transpose. |
Input data is read only from the lower/upper triangle of a , depending on the value of lower . Values from the other triangle are ignored. Output data is returned in the same triangle; the values in the other triangle are implementation-defined and may be anything.
If the number of dimensions of a and b are greater than 2, they are treated as batches of matrices, where all except the minor 2 dimensions are batch dimensions. a and b must have equal batch dimensions.
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - triangular_solve .
Кортеж
See also XlaBuilder::Tuple .
A tuple containing a variable number of data handles, each of which has its own shape.
Tuple(elements)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
elements | vector of XlaOp | N array of type T |
This is analogous to std::tuple in C++. Conceptually:
let v: f32[10] = f32[10]{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
let s: s32 = 5;
let t: (f32[10], s32) = tuple(v, s);
Tuples can be deconstructed (accessed) via the GetTupleElement operation.
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - tuple .
Пока
See also XlaBuilder::While .
While(condition, body, init)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
condition | XlaComputation | XlaComputation of type T -> PRED which defines the termination condition of the loop. |
body | XlaComputation | XlaComputation of type T -> T which defines the body of the loop. |
init | T | Initial value for the parameter of condition and body . |
Sequentially executes the body until the condition fails. This is similar to a typical while loop in many other languages except for the differences and restrictions listed below.
- A
Whilenode returns a value of typeT, which is the result from the last execution of thebody. - The shape of the type
Tis statically determined and must be the same across all iterations.
The T parameters of the computations are initialized with the init value in the first iteration and are automatically updated to the new result from body in each subsequent iteration.
One main use case of the While node is to implement the repeated execution of training in neural networks. Simplified pseudocode is shown below with a graph that represents the computation. The code can be found in while_test.cc . The type T in this example is a Tuple consisting of an int32 for the iteration count and a vector[10] for the accumulator. For 1000 iterations, the loop keeps adding a constant vector to the accumulator.
// Pseudocode for the computation.
init = {0, zero_vector[10]} // Tuple of int32 and float[10].
result = init;
while (result(0) < 1000) {
iteration = result(0) + 1;
new_vector = result(1) + constant_vector[10];
result = {iteration, new_vector};
}
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - while .
Ксор
See also XlaBuilder::Xor .
Performs element-wise XOR of lhs and rhs .
Xor(lhs, rhs)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
The arguments' shapes have to be either similar or compatible. See the broadcasting documentation about what it means for shapes to be compatible. The result of an operation has a shape which is the result of broadcasting the two input arrays. In this variant, operations between arrays of different ranks are not supported, unless one of the operands is a scalar.
An alternative variant with different-dimensional broadcasting support exists for Xor:
Xor(lhs,rhs, broadcast_dimensions)
| Аргументы | Тип | Семантика |
|---|---|---|
| лхс | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| правая сторона | XlaOp | Left-hand-side operand: array of type T |
| broadcast_dimension | ArraySlice | Which dimension in the target shape each dimension of the operand shape corresponds to |
This variant of the operation should be used for arithmetic operations between arrays of different ranks (such as adding a matrix to a vector).
The additional broadcast_dimensions operand is a slice of integers specifying the dimensions to use for broadcasting the operands. The semantics are described in detail on the broadcasting page .
For StableHLO information see StableHLO - xor .









